Refactoring-Improving the Design of Existing Code——学习笔记(5)
Chapter 10 Making Method Calls Simpler
(1)Rename Method
The name of amethod does not reveal its purpose. Change the name of the method.
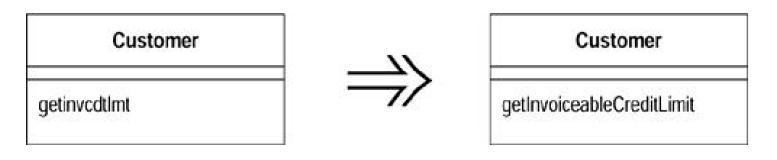
(2)Add Parameter
A method needsmore information from its caller. Add a parameter for an object that can passon this information.

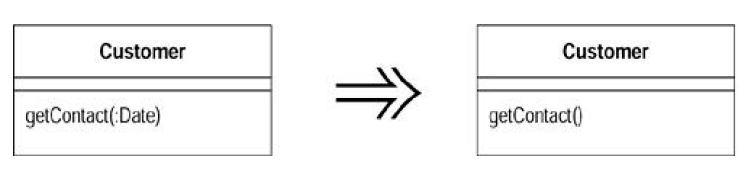
(3)Remove Parameter
A parameter ison longer used by the method body. Remove it.
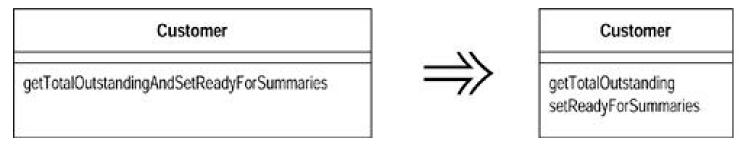
(4)Separate Query from Modifier
You have amethod that returns a value but also changes the state of an object. Create twomethods, one for query and one for the modification.
(5)Parameterize Method
Several methodsdo similar things but with different values contained in the method body.Create one method that uses a parameter for the different values.
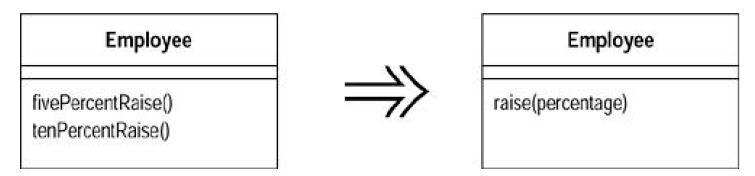
(7)Replace Parameter with Explicit Methods
You have amethod that runs different code depending on the values of an enumeratedparameter. Create a separate method for each value of the parameter.
void setValue (String name,int value) {
if(name.equals(“height”)) {
_height = value;
return;
}
if(name.equals(“width”)) {
_width = value;
return;
}
Assert.shouldneverReachHere();
}
重构后:
void setHeight(int arg) {
_height = arg;
}
void setWidth(int arg) {
_width = arg;
}
(8)Preserve Whole Object
You are gettingseveral values from an object and passing these values as parameters in amethod call. Send the whole object instead.
int low = daysTempRange().getLow();
int high = daysTempRange().getHigh();
withinPlan = plan.withinRange(low,high);
重构后:
withinPlan = plan.withinRange(daysTempRange());
(9)Replace Parameter with Method
An objectinvokes a method, then passes the result as a parameter for a method. Thereceiver can also invoke this method. Remove the parameter and let the receiverinvoke the method.
int basePrice = _quantity * _itemPrice;
discountLevel = getDiscountLevel();
double finalPrice = discountedPrice(basePrice,discountLevel);
重构后:
int basePrice = _quantity *_itemPrice;
double finalPrice = discountedPrice(basePrice);
(10)Introduce Parameter Object
You have a groupof parameters that naturally go together. Replace them with an object.
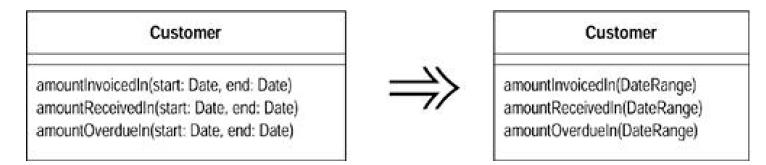
(11)Removing Setting Method
A field shouldbe set at creation time and never altered. Remove any setting method for thatfield.
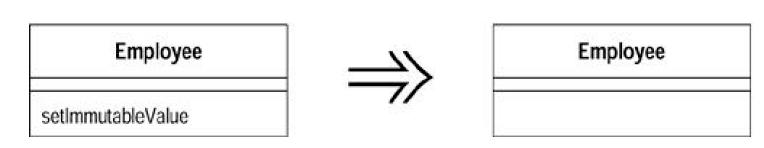
(12)Hide Method
A method is notused by any other class. Make the method private.
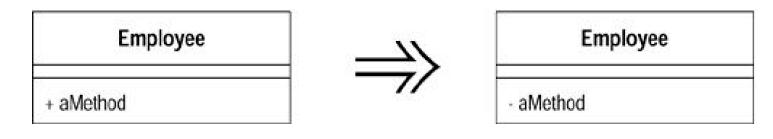
(13)Replace Constructor with Factory Method
You want to domore than simple construction when you create an object. Replace theconstructor with a factory method.
Employee(int type) {
_type=type;
}
重构后:
static Employee create(int type) {
return new Employee(type);
}
(14)Encapsulate Downcast
A method returnsan object that needs to be downcasted by its caller. Move the downcast towithin the method.
Object lastReading() {
return reading.lastElement();
}
重构后:
Reading lastReading() {
return (Reading) readings.lastElement();
}
(15)Replace Error Code with Exception
A method returnsa special code to indicate an error. Throw an exception instead.
int withdraw(int amount) {
if(amount > _balance) {
return -1;
else {
_balance -= amount;
return 0;
}
}
重构后:
void withdraw(int amount) throws BalanceException {
if(amount > _balance) throw new BalanceException();
_balance -= amount;
}
(16)Replace Exception with Test
You are throwingan exception on a condition the caller could have checked first. Change the callerto make the test first.
double getValueForPeriod(int periodNumber) {
try{
return _values[periodNumber];
} catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
return 0;
}
}
重构后:
double getValueForPeriod(int periodNumber) {
if(periodNumber >= _values.length) return 0;
return _values[periodNumber];
}