三星uboot1.1.6源码分析——start.s(5)——与MMU有关的源码(1)
现在接着回到start.s的代码中,进行分析。我省略了一些没用的代码,如与onenand有关的代码。这一篇主要关注MMU有关的代码。
-------------------------------------------------------------
after_copy:
#ifdef CONFIG_ENABLE_MMU ---我们定义了#define CONFIG_ENABLE_MMU
-------------------------------
下面这些很多都涉及到arm的协处理器的操作。

-c0:ID号寄存器
-c0:缓存类型寄存器
-c1:控制寄存器
-c2:转换表基址寄存器(Translation Table Base --TTB)
-c3:域访问控制寄存器—omain access control )
-c4:保留
-c5:异常状态寄存器(fault status -FSR)
-c6:异常地址寄存器(fault address -FAR)
-c7:缓存操作寄存器
-c8:TLB操作寄存器
-c9:缓存锁定寄存器
-c10:TLB 锁定寄存器
-c11-12&14:保留
-c13:处理器ID
-c15:测试配置寄存器
---------------------------------------
主要和两个指令有关mcr和mrc。
MCR 从ARM 寄存器传送数据到协处理器寄存器
MRC 从协处理器寄存器传送数据到ARM 寄存器
MCR 指令将ARM 处理器的寄存器中的数据传送到协处理器的寄存器中.若协处理器不能成功地执行该操作,将产生未定义指令异常中断.指令格式如下;
MCR{cond} coproc,opcodel,Rd,CRn,CRm{,opcode2}
其中
coproc 指令操作的协处理器名.
cpcodel 协处理器的特定操作码.
CRD 作为目标寄存器的协处理器寄存器.
CRn 存放第1 个操作数的协处理器寄存器
CRm 存放第2 个操作数的协处理器寄存器.
Opcode2 可选的协处理器特定操作码.
MCR 指令举例如下:
MCR p6,2,R7,c1,c2,
MCR P7,0,R1,c3,c2,1,
MRC
协处理器寄存器到ARM 寄存器到的数据传送指令.MRC 指令将协处理器寄存器中的
数据传送到ARM 处理器的寄存器中.若协处理器不能成功地执行该操作.将产生未定义
异常中断.指令格式如下.
MRC {cond} coproc,opcodel,Rd,CRn,CRm{,opcode2}
其中coproc 指令操作的协处理器名.
opcodel 协处理器的特定操作码.
CRd 作为目标寄存器的协处理器寄存器.
CRm 存放第2 个操作数的协处理器寄存器.
opcode2 可选的协处理器特定操作码.
MRC 指令举例如下
MRC p5,2,R2,c3,c2
MRC p7,0,R0,c1,c2,1
------------------------------
这个是在ARM7500FE手册上摘录的,我认为有利于理解这两个指令的使用,尤其是下面的例子。
<MCR|MRC>{cond} p#,<expression1>,Rd,cn,cm{,<expression2>}
where:
MRC move from coprocessor to ARM7500FE register (L=1)
MCR move from ARM7500FE register to coprocessor (L=0)
{cond} two character condition mnemonic
p# the unique number of the required coprocessor
<expression1> evaluated to a constant and placed in the CP Opc ?eld
Rd is an expression evaluating to a valid ARM processor register
number
cn and cm are expressions evaluating to the valid coprocessor register
numbers CRn and CRm respectively
<expression2> where present is evaluated to a constant and placed in
the CP ?eld
MRC 2,5,R3,c5,c6 ; request coproc 2 to perform operation 5
;on c5 and c6, and transfer the (single
;32-bit word) result back to R3
MCR 6,0,R4,c6 ;request coproc 6 to perform operation 0
;on R4 and place the result in c6
MRCEQ 3,9,R3,c5,c6,2 ;conditionally request coproc 2 to
;perform
;operation 9 (type 2) on c5 and c6, and
;transfer the result back to R3
-----------------------------------
enable_mmu:
-----------------------------------------------------------
/* enable domain access */
ldr r5, =0x0000ffff
mcr p15, 0, r5, c3, c0, 0@ load domain access register
-------------------------------------------------------------
上面这个主要与c3有关,如下所示:c3, Domain Access Control Register
The purpose of the Domain Access Control Register is to hold the access permissions for a maximum of 16 domains.
Table 3.59 lists the purposes of the individual bits in the Domain Access Control Register.
The Domain Access Control Register is:
in CP15 c3
a 32-bit read/write register banked for Secure and Non-secure worlds
accessible in privileged modes only.
Figure 3.35 shows the bit arrangement of the Domain Access Control Register.
Figure 3.35. Domain Access Control Register format
Table 3.59 lists how the bit values correspond with the Domain Access Control Register functions.
Table 3.59. Domain Access Control Register bit functions
The purpose of the fields D15-D0 in the register is to define the access permissions for each one of the 16 domains. These domains can be either sections, large pages or small pages of memory:
b00 = No access, reset value. Any access generates a domain fault.
b01 = Client. Accesses are checked against the access permission bits in the TLB entry.
b10 = Reserved. Any access generates a domain fault.
b11 = Manager. Accesses are not checked against the access permission bits in the TLB entry, so a permission fault cannot be generated.
[a] n is the Domain number in the range between 0 and 15
Attempts to write to this register in Secure Privileged mode when
Table 3.60. Results of access to the Domain Access Control Register
To use the Domain Access Control Register read or write CP15 c3 with:
Opcode_1 set to 0
CRn set to c3
CRm set to c0
Opcode_2 set to 0.
For example:
MRC p15, 0, <Rd>, c3, c0, 0 ; Read Domain Access Control Register
MCR p15, 0, <Rd>, c3, c0, 0 ; Write Domain Access Control Register
-------------------------------------------------------------
/* Set the TTB register */
ldr r0, _mmu_table_base
ldr r1, =CFG_PHY_UBOOT_BASE
ldr r2, =0xfff00000
bic r0, r0, r2
orr r1, r0, r1
mcr p15, 0, r1, c2, c0, 0---------------------------------------------------
c2, Translation Table Base Register 0(摘于ARM手册)
The purpose of the Translation Table Base Register 0 is to hold the physical address of the first-level translation table.
You use Translation Table Base Register 0 for process-specific addresses, where each process maintains a separate first-level page table. On a context switch you must modify both Translation Table Base Register 0 and the Translation Table Base Control Register, if appropriate.
Table 3.53 lists the purposes of the individual bits in the Translation Table Base Register 0.
The Translation Table Base Register 0 is:
in CP15 c2
a 32 bit read/write register banked for Secure and Non-secure worlds
accessible in privileged modes only.
Figure 3.32 shows the bit arrangement for the Translation Table Base Register 0.
Figure 3.32. Translation Table Base Register 0 format
Table 3.53 lists how the bit values correspond with the Translation Table Base Register 0 functions.
Table 3.53. Translation Table Base Register 0 bit functions
Indicates the Outer cacheable attributes for page table walking:
b00 = Outer Noncacheable, reset value
b01 = Write-back, Write Allocate
b10 = Write-through, No Allocate on Write
b11 = Write-back, No Allocate on Write.
[2]PIf the processor supports ECC, it indicates to the memory controller it is enabled or disabled. For ARM1176JZ-S processors this is 0:
0 =
[a] For an explanation of N see c2, Translation Table Base Control Register.
Attempts to write to this register in Secure Privileged mode when
Table 3.54. Results of access to the Translation Table Base Register 0
A write to the Translation Table Base Register 0 updates the address of the first level translation table from the value in bits [31:7] of the written value, to account for the maximum value of 7 for N. The number of bits of this address that the processor uses, and therefore, the required alignment of the first level translation table, depends on the value of N, see c2, Translation Table Base Control Register.
A read from the Translation Table Base Register 0 returns the complete address of the first level translation table in bits [31:7] of the read value, regardless of the value of N.
To use the Translation Table Base Register 0 read or write CP15 c2 with:
Opcode_1 set to 0
CRn set to c2
CRm set to c0
Opcode_2 set to 0.
For example:
MRC p15, 0, <Rd>, c2, c0, 0 ; Read Translation Table Base Register 0
MCR p15, 0, <Rd>, c2, c0, 0 ; Write Translation Table Base Register 0
Note
The ARM1176JZ-S processor cannot page table walk from level one cache. Therefore, if C is set to 1, to ensure coherency, you must either store page tables in Inner write-through memory or, if in Inner write-back, you must clean the appropriate cache entries after modification so that the mechanism for the hardware page table walks sees them.
--------------------------------------------------
/* Enable the MMU */
mmu_on:
mrc p15, 0, r0, c1, c0, 0
orr r0, r0, #1/*Set CR_M to enable MMU */
mcr p15, 0, r0, c1, c0, 0
nop
nop
nop
nop
#endif-----------------------------------------------------------
主要和c1有关,如下所示:
c1, Control Register
Purpose of the Control Register
The purpose of the Control Register is to provide control and configuration of:
memory alignment, endianness, protection, and fault behavior
MMU and cache enables and cache replacement strategy
interrupts and the behavior of interrupt latency
the location for exception vectors
program flow prediction.

Use of the Control Register
To use the Control Register it is recommended that you use a read modify write technique. To use the Control Register read or write CP15 with:
Opcode_1 set to 0
CRn set to c1
CRm set to c0
Opcode_2 set to 0.
For example:
MRC p15, 0, <Rd>, c1, c0, 0 ; Read Control Register configuration data
MCR p15, 0, <Rd>, c1, c0, 0 ; Write Control Register configuration data
Normally, to set the V bit and the B, EE, and U bits you configure signals at reset.
-----------------------------------------------------------
下面是我在ARM手册中找到的有关MMU协处理器的资料:
MMU control and configuration(摘于ARM手册)
The purpose of the MMU control and configuration registers is to:
allocate physical address locations from the Virtual Addresses (VAs) that the processor generates.
control program access to memory.
designate areas of memory as either:
Noncacheable
unbufferable
Noncacheable and unbufferable.
detect MMU faults and external aborts
hold thread and process IDs
provide direct access to the TLB lockdown entries.
The MMU control and configuration registers consist of one 32-bit read-only register, one 32-bit write-only register, and 22 32-bit read/write registers. Figure 3.2 shows the arrangement of registers in this functional group.
Figure 3.2. MMU control and configuration registers
as a set of numbers, values that describe aspects of the MMU or indicate its current state
as a set of addresses for tables in memory
as a set of operations that act on the MMU.
----------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------
总结:MCR和MRC两个指令对p15协处理器的操作方法:
MCR{cond} P15,<Opcode_1>,<Rd>,<CRn>,<CRm>,<Opcode_2>MRC{cond} P15,<Opcode_1>,<Rd>,<CRn>,<CRm>,<Opcode_2>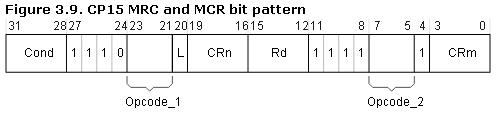
<opcode_1>:协处理器行为操作码,对于CP15来说,<opcode_1>永远为0b000,否则结果未知。
<Rd>:不能是r15/pc,否则,结果未知。
<crn>:作为目标寄存器的协处理器寄存器,编号为C0~C15。
<crm>:附加的目标寄存器或源操作数寄存器,如果不需要设置附加信息,将crm设置为c0,否则结果未知。
<opcode_2>:提供附加信息比如寄存器的版本号或者访问类型,用于区分同一个编号的不同物理寄存器,可以省略<opcode_2>或者将其设置为0,否则结果未知。

