【原】java定时器简单了解
前几看了一下《thinking in java》了解到java原生的Times类有两个问题:
(1)Timer是启动单个线程来处理所有的时间任务,如果一个任务耗时很久,那么如果在执行这个过程中,下个定时任务开始,就会对接下来的任务造成影响;
(2)Timer某一个定时程序在执行过程中抛出运行时异常,那么定时器就会以为终止定时器的运行;
?
首先了解一下Timer类的核心组成
?
Timer有两个核心的属性,一个是TaskQueue对象,用于存储任务队列,一个是TimerThread,用于执行队列中的任务。
?
public class Timer { private TaskQueue queue = new TaskQueue(); private TimerThread thread = new TimerThread(queue); 。。。。。。?
?
写代码验证一下,看看是否是这样的。
Timer和TimeTask是java基础中实现定时程序的两个核心类。
A、TimerTask是一个抽象类,内部实现了Runnable接口,同时定义了任务的几个状态;
B、Timer类来负责调度继承TimerTask的具体任务,可是实现定时或者指定周期运行
?
通过打印可以发现,代码是顺序执行的,最简单的代码实现:
public class TimerTest extends TimerTask{public static void main(String[] args) {Timer timer1 = new Timer("time1");timer1.schedule(new TimerTest(), 1);timer1.schedule(new TimerTest(), 2);timer1.schedule(new TimerTest(), 3);}@Overridepublic void run() {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-线程暂停5秒");TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-线程执行结束");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}??当代码运行中,第一个任务出现NullPointException时,第二个任务就不会再运行下去。
public class TimerTest extends TimerTask{public static void main(String[] args) {Timer timer1 = new Timer("time1");timer1.schedule(new TimerTest(), 1);timer1.schedule(new TimerTest(), 2);}@Overridepublic void run() {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-线程暂停5秒");TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-线程执行结束");String aaa = null;System.out.println(aaa.hashCode());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}?
Timer有三部分组成:
任务单元,任务队列,任务调度器,从下图能够非常直观的看出几个类直接的关系。
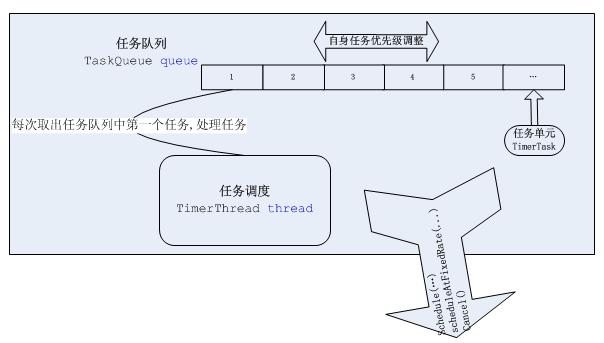
?
?
?
TaskQueue任务队列的管理:
?
?
一个具有优先级的时间任务队列,通过下次执行时间来进行排序。实际上就是一个数组,数据里面放着了TimeTask对象。
?
void add(TimerTask task) { if (size + 1 == queue.length) queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, 2*queue.length); queue[++size] = task; fixUp(size); }?
?上面是TaskQueue中的add方法,添加新的TimeTask的时候,首先判断是否超出了数组长度,初始数组是128,如果超过,就将数组长度加倍。
最后执行fixUp,重新将数组进行排序,TimeTask中nextExecutionTime小的排在数组的最前面,即最近一个要执行的定时任务。
?
?
Timer中重载了这个方法schedule,用来实现不同场景的任务调度,每一个schedule方法中都是用了这个方法sched
?
private void sched(TimerTask task, long time, long period) { if (time < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal execution time."); synchronized(queue) { if (!thread.newTasksMayBeScheduled) throw new IllegalStateException("Timer already cancelled."); synchronized(task.lock) { if (task.state != TimerTask.VIRGIN) throw new IllegalStateException( "Task already scheduled or cancelled"); task.nextExecutionTime = time; task.period = period; task.state = TimerTask.SCHEDULED; } queue.add(task); if (queue.getMin() == task) queue.notify(); } }?
?从上述代码中可以看出,首先锁住任务队列,如果task符合条件,则直接将任务加入到任务队列中,并设置好任务下次执行时间以及执行周期并设置状态为可以被调度。
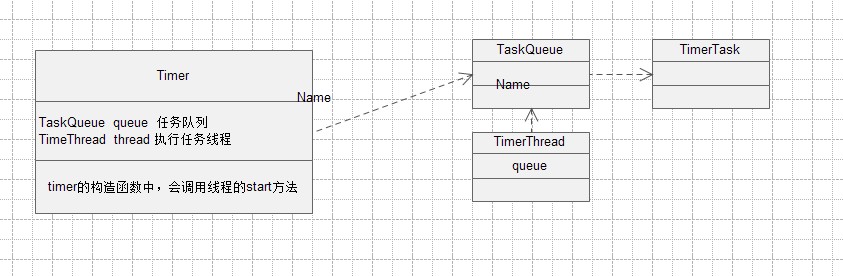
?
?
鉴于 Timer 的上述缺陷,Java 5 推出了基于线程池设计的 ScheduledExecutor。其设计思想是,每一个被调度的任务都会由线程池中一个线程去执行,因此任务是并发执行的,相互之间不会受到干扰。
?
java.util.courrent包中有一个定时调度线程的类:ScheduledExecutorService
下面的这个例子,从执行结果来看,两个定时程序是并发执行的,并且一个定时程序执行如果抛出异常,对于下个任务的执行没有啥影响,照样执行下去。
public class CourrentTimer implements Runnable {
public static void main(String[] args) {CourrentTimer timer = new CourrentTimer();ScheduledExecutorService executer = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2); //创建线程池,调用ThreadPoolExecutor来进行创建,通过BlockingQueue来管理任务队列executer.submit(timer);executer.submit(timer); //Timer类实现Runnable接口,从而进入任务队列}@Overridepublic void run() {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-线程暂停5秒后运行-"+new Date());String aa = null;System.out.println(aa.hashCode());} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}??下面是执行返回的结果
?
public interface Job { //在Trigger配置下通过scheduler来进行调度的具体任务 public void execute(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException; //任务的上下文对象,包含了任务执行细节中的各个情况}?
?
Spring和Quartz的整合,可以通过简单扼配置,就能完成负责的时间调度任务,对于应用来说,只需要实现具体的任务即可,时间的调度等等细节交由Quartz来执行。
下面通过一个简单的例子来说明:
?
</property><property name="cronExpression">
<value>0 30 2 * * ? *</value>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 总管理类 如果将lazy-init='false'那么容器启动就会执行调度程序 ,任务的调度器 -->
<bean id="startQuertz" lazy-init="false" autowire="no" />
</list>
</property>
</bean>
?
?
? ? timeTask俗称TT,是淘宝内部封装的一个时间调度器,Spring Quartz可以快速的完成时间的调度,但是如果应用是在集群环境下,我们就希望有一台机器来完成定时的任务,如果每台机器跑的代码完成一样,那么这个定时器就会在每台机器上都跑一边,如果跑的业务流程是幂等的还好,如果不是,那就会很多问题,TT能够实现的一个简单功能是,定时程序可以通过后台页面点击触发,能够制定集群中的一台机器来运行,具体原理介绍一下。
?
?
综合上面的一些结论,受到的一些启发:
?
?
(1)抽象任务接口,通过实现任务接口,来满足各种各样任务的需要,从而满足业务场景(2)任务队列,存放实现任务接口的业务任务
(3)任务调度单独抽象,用来调度任务的执行
(4)抽象规则,定时任务有个规则就是定时程序啥时候执行,将这个设置抽象成一个简单的设置,通过一些表达式,来完成,简单高效?
?
?
?
?
?
参考资料:
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-taskschedule/
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-timer/
http://xxxxxxxx-rui.iteye.com/blog/998603
?
?