读logback源码系列文章(二)——提供ILoggerFactory
上篇博客介绍了logback是怎么对接slf4j的,简言之,就是通过下面这行代码
return StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton().getLoggerFactory();
slf4j委托具体实现框架的StaticLoggerBinder来返回一个ILoggerFactory,从而对接到具体实现框架上
这篇博客就接下来介绍一下,logback的StaticLoggerBinder类是怎么创建ILoggerFactory的
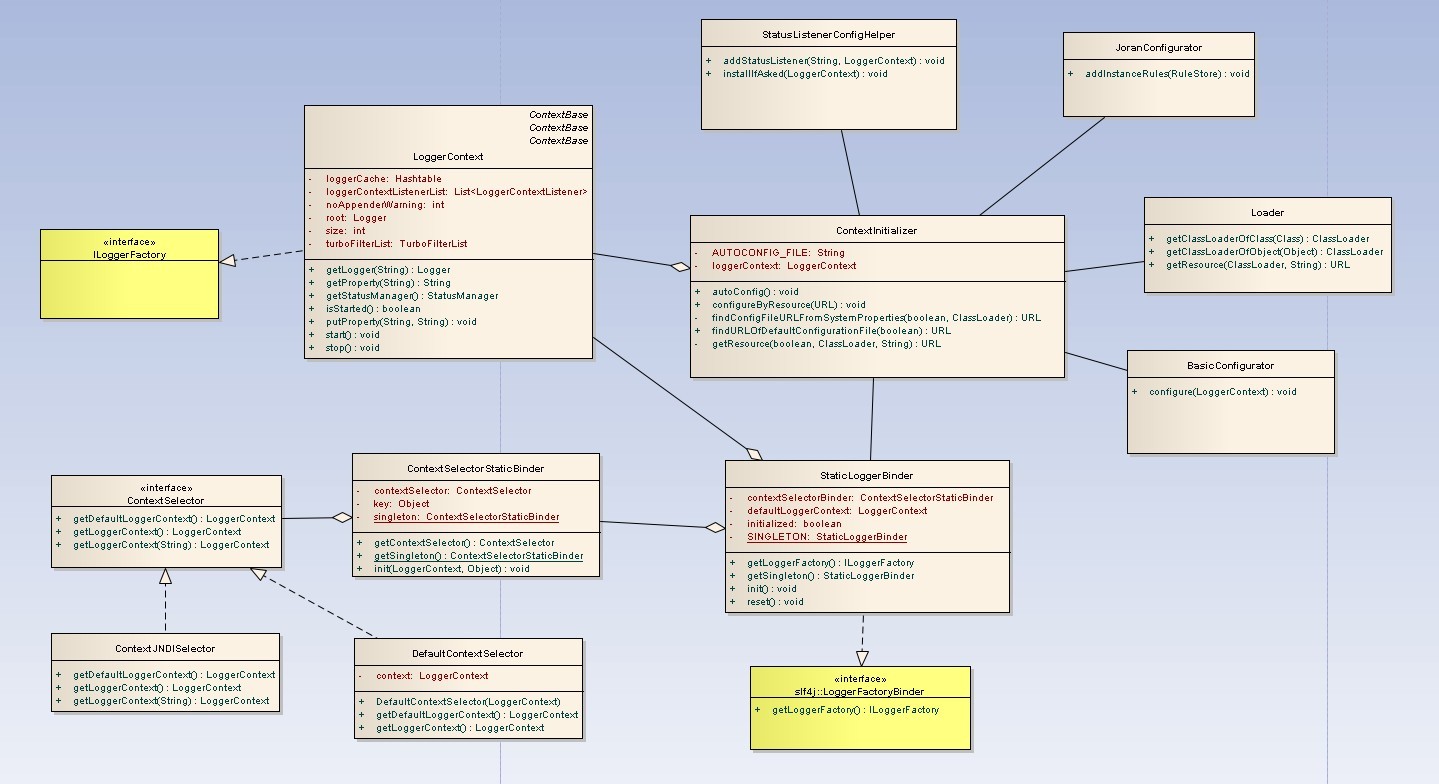
在图中可以看到,在logback里,ILoggerFactory的实现类是LoggerContext
logback的StaticLoggerBinder类实现了LoggerFactoryBinder接口,这个接口有两个方法
public interface LoggerFactoryBinder { /** * Return the instance of {@link ILoggerFactory} that * {@link org.slf4j.LoggerFactory} class should bind to. * * @return the instance of {@link ILoggerFactory} that * {@link org.slf4j.LoggerFactory} class should bind to. */ public ILoggerFactory getLoggerFactory(); /** * The String form of the {@link ILoggerFactory} object that this * <code>LoggerFactoryBinder</code> instance is <em>intended</em> to return. * * <p>This method allows the developer to intterogate this binder's intention * which may be different from the {@link ILoggerFactory} instance it is able to * yield in practice. The discrepency should only occur in case of errors. * * @return the class name of the intended {@link ILoggerFactory} instance */ public String getLoggerFactoryClassStr();}其中比较重要的是getLoggerFactory()方法,其实自定义的StaticLoggerBinder类不实现这个接口也是可以的,只要能保证提供getLoggerFactory()方法,并返回一个ILoggerFactory就可以了
下面就来具体地看看StaticLoggerBinder类的代码:
首先,该类必须有一个getSingleton()方法,来返回该类的单例
private static StaticLoggerBinder SINGLETON = new StaticLoggerBinder();
public static StaticLoggerBinder getSingleton() { return SINGLETON; }以上代码用了比较简单的单例模式,提供getSingleton()方法是对接slf4j的强制要求
然后这个类用了一个static块来保证初始化
static { SINGLETON.init(); }void init() { try { try { new ContextInitializer(defaultLoggerContext).autoConfig(); } catch (JoranException je) { Util.report("Failed to auto configure default logger context", je); } StatusPrinter.printInCaseOfErrorsOrWarnings(defaultLoggerContext); contextSelectorBinder.init(defaultLoggerContext, KEY); initialized = true; } catch (Throwable t) { // we should never get here Util.report("Failed to instantiate [" + LoggerContext.class.getName() + "]", t); } }这个初始化方法init()里做了2件事
第一件事是委托ContextInitializer类对defaultLoggerContext进行初始化。这里如果找到了任一配置文件,就会根据配置文件去初始化LoggerContext,如果没找到,会使用默认配置。关于LoggerContext是怎么根据配置文件进行配置的,在后面的博客中介绍,这里先略过
第二件事是对ContextSelectorStaticBinder类进行初始化
public void init(LoggerContext defaultLoggerContext, Object key) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException { if(this.key == null) { this.key = key; } else if (this.key != key) { throw new IllegalAccessException("Only certain classes can access this method."); } String contextSelectorStr = OptionHelper .getSystemProperty(ClassicConstants.LOGBACK_CONTEXT_SELECTOR); if (contextSelectorStr == null) { contextSelector = new DefaultContextSelector(defaultLoggerContext); } else if (contextSelectorStr.equals("JNDI")) { // if jndi is specified, let's use the appropriate class contextSelector = new ContextJNDISelector(defaultLoggerContext); } else { contextSelector = dynamicalContextSelector(defaultLoggerContext, contextSelectorStr); } }如果系统参数中配置了JNDI,这里会得到一个ContextJNDISelector,实际应用中,一般会得到一个DefaultContextSelector,并且把已经初始化完成的defaultLoggerContext传给新创建的这个DefaultContextSelector
经过上面的步骤,StaticLoggerBinder的init()方法就走完了,接下来就会调用到关键的getLoggerFactory()方法
public ILoggerFactory getLoggerFactory() { if (!initialized) { return defaultLoggerContext; } if (contextSelectorBinder.getContextSelector() == null) { throw new IllegalStateException( "contextSelector cannot be null. See also " + NULL_CS_URL); } return contextSelectorBinder.getContextSelector().getLoggerContext(); }可以看到,这里有2条分支,如果initialized是false,那么会直接返回defaultLoggerContext。否则就委托刚才提到的ContextSelectorStaticBinder返回一个ContextSelector(一般就是DefaultContextSelector),然后由ContextSelector来返回LoggerContext
public class DefaultContextSelector implements ContextSelector { private LoggerContext context; public DefaultContextSelector(LoggerContext context) { this.context = context; } public LoggerContext getLoggerContext() { return getDefaultLoggerContext(); } public LoggerContext getDefaultLoggerContext() { return context; }}可以看到,代码有点绕,不过逻辑还是很清楚的
总结一下这个过程:
1、StaticLoggerBinder在加载的时候,会去读取配置文件,并根据配置文件对LoggerContext进行初始化
2、然后初始化ContextSelectorStaticBinder,在这个类内部new一个DefaultContextSelector,并把第一步中配置完毕的LoggerContext传给DefaultContextSelector
3、调用getLoggerFactory()方法,直接返回第一步中配置的LoggerContext,或者委托DefaultContextSelector类返回LoggerContext