(转)JMX 入门例子
转自:http://rabbit9898.iteye.com/blog/1009198
?
?? JMX(Java Management Extensions,即Java管理扩展)是一个为应用程序、设备、系统等植入管理功能的框架。JMX可以跨越一系列异构操作系统平台、系统体系结构和网络传输协议,灵活的开发无缝集成的系统、网络和服务管理应用。
?
我们还是从JMX能给我们提供什么好处入手来理解吧。举一个应用实例:在一个系统中常常会有一些配置信息,比如服务的IP地址,端口号什么的,那么如何来写这些代码呢?
1、初级程序员一般是写死在程序里,到要改变时就去改程序,然后再编译发布;
2、程序熟手则一般把这些信息写在一个配置文件里(JAVA一般都是*.properties文件),
??? 到要改变时只要改配置文件,但还是重新启动系统,以便读取配置文件里的新值;
3、程序好手则会写一个段代码,把配置值缓存起来,系统在读值的时候,先看看配置文件有
??? 没有更动。如有更改则重读一遍,否则从缓存里读取值
4、程序高手则懂得取物为我所用,用JMX!把配置属性集中在一个类,然后写一个叫MBean
??? 的东东,再配置一下就轻松搞定了。而且JMX自动提供了一个WEB页面来给你来改变这些
??? 配置信息。
?
参考Java提供的例子(需要 jdk1.6):
http://download.oracle.com/javase/6/docs/technotes/guides/jmx/examples.html
?
1. 需要被管理类的接口? HelloMBean.java? (规范一般是***MBean.java)
?
? /* HelloMBean.java - MBean interface describing the management operations and attributes for the Hello World MBean. In this case there are two operations, "sayHello" and "add", and two attributes, "Name" and "CacheSize". */package com.example.mbeans;public interface HelloMBean { // operations public void sayHello(); public int add(int x, int y); // attributes // a read-only attribute called Name of type String public String getName(); // a read-write attribute called CacheSize of type int public int getCacheSize(); public void setCacheSize(int size);}
/* HelloMBean.java - MBean interface describing the management operations and attributes for the Hello World MBean. In this case there are two operations, "sayHello" and "add", and two attributes, "Name" and "CacheSize". */package com.example.mbeans;public interface HelloMBean { // operations public void sayHello(); public int add(int x, int y); // attributes // a read-only attribute called Name of type String public String getName(); // a read-write attribute called CacheSize of type int public int getCacheSize(); public void setCacheSize(int size);}?
2. 需要管理的类? Hello.java? (通常是实现**MBean.java)
? /* Hello.java - MBean implementation for the Hello World MBean. 因篇幅所限,把examples带的注释去掉了,自己可以下载看 */package com.example.mbeans;public class Hello implements HelloMBean { public void sayHello() {System.out.println("hello, world"); } public int add(int x, int y) {return x + y; } public String getName() {return this.name; } public int getCacheSize() {return this.cacheSize; } public synchronized void setCacheSize(int size) {this.cacheSize = size;System.out.println("Cache size now " + this.cacheSize); } private final String name = "Reginald"; private int cacheSize = DEFAULT_CACHE_SIZE; private static final int DEFAULT_CACHE_SIZE = 200;}
/* Hello.java - MBean implementation for the Hello World MBean. 因篇幅所限,把examples带的注释去掉了,自己可以下载看 */package com.example.mbeans;public class Hello implements HelloMBean { public void sayHello() {System.out.println("hello, world"); } public int add(int x, int y) {return x + y; } public String getName() {return this.name; } public int getCacheSize() {return this.cacheSize; } public synchronized void setCacheSize(int size) {this.cacheSize = size;System.out.println("Cache size now " + this.cacheSize); } private final String name = "Reginald"; private int cacheSize = DEFAULT_CACHE_SIZE; private static final int DEFAULT_CACHE_SIZE = 200;}?
?
3. 代理/注册类 Main.java
?
 package com.example.mbeans;import java.lang.management.*;import javax.management.*;public class Main { /* For simplicity, we declare "throws Exception". Real programs will usually want finer-grained exception handling. */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// Get the Platform MBean ServerMBeanServer mbs = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer();// Construct the ObjectName for the MBean we will registerObjectName name = new ObjectName("com.example.mbeans:type=Hello");// Create the Hello World MBeanHello mbean = new Hello();// Register the Hello World MBeanmbs.registerMBean(mbean, name);// Wait foreverSystem.out.println("Waiting forever...");Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE); }}
package com.example.mbeans;import java.lang.management.*;import javax.management.*;public class Main { /* For simplicity, we declare "throws Exception". Real programs will usually want finer-grained exception handling. */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// Get the Platform MBean ServerMBeanServer mbs = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer();// Construct the ObjectName for the MBean we will registerObjectName name = new ObjectName("com.example.mbeans:type=Hello");// Create the Hello World MBeanHello mbean = new Hello();// Register the Hello World MBeanmbs.registerMBean(mbean, name);// Wait foreverSystem.out.println("Waiting forever...");Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE); }}?
4. 编译、测试运行上面的程序
?
javac com/example/mbeans/*.java
# 启动程序
java com.example.mbeans.Main
另起一个命令行或者cmd:
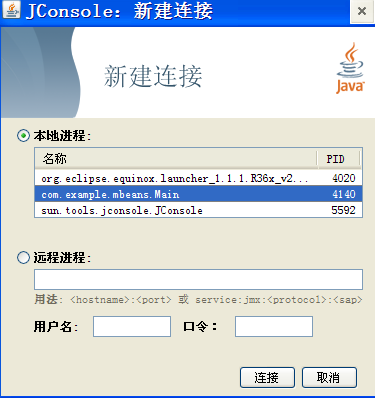
运行jconsole? (# JConsole is located in $(J2SE_HOME)/bin/jconsole) 可以看到,选择本地的进程 com.example.mbeans 连接 就可以进行管理了。
?
?
管理界面:
?

?