cocos2d学习笔记(七)物理引擎box2d之一
一、准备工作
引入box2d包,在需要使用box2d的文件中加入box2d的头文件;由于box2d是c++编写的,所以要把引入box2d的所有文件后缀名都改为.mm
二、box2d中的一些重要参数
1、gravity,重力加速度,同现实世界中的g,向量
2、shape,形状,形状是有大小的
3、density,密度
4、friction,摩擦力
5、restitution,恢复,此参数用于碰撞,如果两个物体有不同的restitution,box2d总是选择比较大的restitution进行计算
6、meter,距离单位,灵活定义你的meter,当对象为0.1至10meters的时候,box2d可以很好的处理它们,
三、box2d之hello world
让我们先创建一个box2d项目。创建好之后运行:
每当我们点击屏幕时,会落下一个小方块,ok,然我们来详细看下生成的代码。
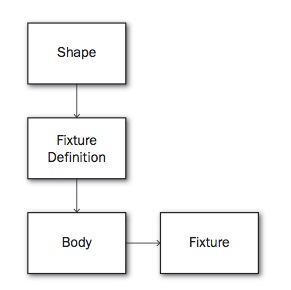
创建fixture步骤
知道了这些,让我们来看看如何创建一个box2d世界中的物体
-(void) tick: (ccTime) dt{//It is recommended that a fixed time step is used with Box2D for stability//of the simulation, however, we are using a variable time step here.//You need to make an informed choice, the following URL is useful//http://gafferongames.com/game-physics/fix-your-timestep/int32 velocityIterations = 8;int32 positionIterations = 1;// Instruct the world to perform a single step of simulation. It is// generally best to keep the time step and iterations fixed.world->Step(dt, velocityIterations, positionIterations);//Iterate over the bodies in the physics worldfor (b2Body* b = world->GetBodyList(); b; b = b->GetNext()){if (b->GetUserData() != NULL) {//Synchronize the AtlasSprites position and rotation with the corresponding bodyCCSprite *myActor = (CCSprite*)b->GetUserData();myActor.position = CGPointMake( b->GetPosition().x * PTM_RATIO, b->GetPosition().y * PTM_RATIO);myActor.rotation = -1 * CC_RADIANS_TO_DEGREES(b->GetAngle());}}}
先说下step方法,velocityIterations和positionIterations这两个参数越大,box2d就能进行更好的模拟,但是性能就会下降,这两个参数你应该自己把握以适合你的游戏。下面的循环是为了让你的sprite与box2d中的对象同步,你可以注释掉这段代码看下效果,你会发现粉方块掉下去了,你的sprite没掉下去。
ok,今天先这么多,没想到想着挺简单,却写了这么久,有时间继续!