linux 内核poll/select/epoll实现剖析
f_ops.poll和wait_queue
poll/select/epoll的实现都是基于文件提供的poll方法(f_op->poll),
该方法利用poll_table提供的_qproc方法向文件内部事件掩码_key对应的的一个或多个等待队列(wait_queue_head_t)上添加包含唤醒函数(wait_queue_t.func)的节点(wait_queue_t),并检查文件当前就绪的状态返回给poll的调用者(依赖于文件的实现)。
当文件的状态发生改变时(例如网络数据包到达),文件就会遍历事件对应的等待队列并调用回调函数(wait_queue_t.func)唤醒等待线程。
通常的file.f_ops.poll实现及相关结构体如下
struct file { const struct file_operations*f_op; spinlock_tf_lock; // 文件内部实现细节 void *private_data;#ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL /* Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file */ struct list_headf_ep_links; struct list_headf_tfile_llink;#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL */ // 其他细节....};// 文件操作struct file_operations { // 文件提供给poll/select/epoll // 获取文件当前状态, 以及就绪通知接口函数 unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *); // 其他方法read/write 等... ...};// 通常的file.f_ops.poll 方法的实现unsigned int file_f_op_poll (struct file *filp, struct poll_table_struct *wait){ unsigned int mask = 0; wait_queue_head_t * wait_queue; //1. 根据事件掩码wait->key_和文件实现filep->private_data 取得事件掩码对应的一个或多个wait queue head some_code(); // 2. 调用poll_wait 向获得的wait queue head 添加节点 poll_wait(filp, wait_queue, wait); // 3. 取得当前就绪状态保存到mask some_code(); return mask;}// select/poll/epoll 向文件注册就绪后回调节点的接口结构typedef struct poll_table_struct { // 向wait_queue_head 添加回调节点(wait_queue_t)的接口函数 poll_queue_proc _qproc; // 关注的事件掩码, 文件的实现利用此掩码将等待队列传递给_qproc unsigned long _key;} poll_table;typedef void (*poll_queue_proc)(struct file *, wait_queue_head_t *, struct poll_table_struct *);// 通用的poll_wait 函数, 文件的f_ops->poll 通常会调用此函数static inline void poll_wait(struct file * filp, wait_queue_head_t * wait_address, poll_table *p){ if (p && p->_qproc && wait_address) { // 调用_qproc 在wait_address 上添加节点和回调函数 // 调用 poll_table_struct 上的函数指针向wait_address添加节点, 并设置节点的func // (如果是select或poll 则是 __pollwait, 如果是 epoll 则是 ep_ptable_queue_proc), p->_qproc(filp, wait_address, p); }}// wait_queue 头节点typedef struct __wait_queue_head wait_queue_head_t;struct __wait_queue_head { spinlock_t lock; struct list_head task_list;};// wait_queue 节点typedef struct __wait_queue wait_queue_t;struct __wait_queue { unsigned int flags;#define WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE0x01 void *private; wait_queue_func_t func; struct list_head task_list;};typedef int (*wait_queue_func_t)(wait_queue_t *wait, unsigned mode, int flags, void *key);// 当文件的状态发生改变时, 文件会调用此函数,此函数通过调用wait_queue_t.func通知poll的调用者// 其中key是文件当前的事件掩码void __wake_up(wait_queue_head_t *q, unsigned int mode, int nr_exclusive, void *key){ unsigned long flags; spin_lock_irqsave(&q->lock, flags); __wake_up_common(q, mode, nr_exclusive, 0, key); spin_unlock_irqrestore(&q->lock, flags);}static void __wake_up_common(wait_queue_head_t *q, unsigned int mode, int nr_exclusive, int wake_flags, void *key){ wait_queue_t *curr, *next; // 遍历并调用func 唤醒, 通常func会唤醒调用poll的线程 list_for_each_entry_safe(curr, next, &q->task_list, task_list) { unsigned flags = curr->flags; if (curr->func(curr, mode, wake_flags, key) && (flags & WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE) && !--nr_exclusive) { break; } }}?poll 和 selectpoll和select的实现基本上是一致的,只是传递参数有所不同,他们的基本流程如下:
1. 复制用户数据到内核空间
2. 估计超时时间
3. 遍历每个文件并调用f_op->poll 取得文件当前就绪状态, 如果前面遍历的文件都没有就绪,向文件插入wait_queue节点
4. 遍历完成后检查状态:
??????? a). 如果已经有就绪的文件转到5;
??????? b). 如果有信号产生,重启poll或select(转到 1或3);
??????? c). 否则挂起进程等待超时或唤醒,超时或被唤醒后再次遍历所有文件取得每个文件的就绪状态
5. 将所有文件的就绪状态复制到用户空间
6. 清理申请的资源
?
关键结构体?下面是poll/select共用的结构体及其相关功能:
poll_wqueues 是?select/poll 对poll_table接口的具体化实现,其中的table, inline_index和inline_entries都是为了管理内存。
poll_table_entry 与一个文件相关联,用于管理插入到文件的wait_queue节点。
// select/poll 对poll_table的具体化实现struct poll_wqueues { poll_table pt; struct poll_table_page *table; // 如果inline_entries 空间不足, 从poll_table_page 中分配 struct task_struct *polling_task; // 调用poll 或select 的进程 int triggered; // 已触发标记 int error; int inline_index; // 下一个要分配的inline_entrie 索引 struct poll_table_entry inline_entries[N_INLINE_POLL_ENTRIES];//};// 帮助管理select/poll 申请的内存struct poll_table_page { struct poll_table_page * next; // 下一个 page struct poll_table_entry * entry; // 指向第一个entries struct poll_table_entry entries[0];};// 与一个正在poll /select 的文件相关联,struct poll_table_entry { struct file *filp; // 在poll/select中的文件 unsigned long key; wait_queue_t wait; // 插入到wait_queue_head_t 的节点 wait_queue_head_t *wait_address; // 文件上的wait_queue_head_t 地址};?
公共函数?下面是poll/select公用的一些函数,这些函数实现了poll和select的核心功能。
poll_initwait 用于初始化poll_wqueues,
__pollwait 实现了向文件中添加回调节点的逻辑,
pollwake 当文件状态发生改变时,由文件调用,用来唤醒线程,
poll_get_entry,free_poll_entry,poll_freewait用来申请释放poll_table_entry 占用的内存,并负责释放文件上的wait_queue节点。
?
// poll_wqueues 的初始化:// 初始化 poll_wqueues , __pollwait会在文件就绪时被调用void poll_initwait(struct poll_wqueues *pwq){ // 初始化poll_table, 相当于调用基类的构造函数 init_poll_funcptr(&pwq->pt, __pollwait); /* * static inline void init_poll_funcptr(poll_table *pt, poll_queue_proc qproc) * { * pt->_qproc = qproc; * pt->_key = ~0UL; * } */ pwq->polling_task = current; pwq->triggered = 0; pwq->error = 0; pwq->table = NULL; pwq->inline_index = 0;}// wait_queue设置函数// poll/select 向文件wait_queue中添加节点的方法static void __pollwait(struct file *filp, wait_queue_head_t *wait_address, poll_table *p){ struct poll_wqueues *pwq = container_of(p, struct poll_wqueues, pt); struct poll_table_entry *entry = poll_get_entry(pwq); if (!entry) { return; } get_file(filp); //put_file() in free_poll_entry() entry->filp = filp; entry->wait_address = wait_address; // 等待队列头 entry->key = p->key; // 设置回调为 pollwake init_waitqueue_func_entry(&entry->wait, pollwake); entry->wait.private = pwq; // 添加到等待队列 add_wait_queue(wait_address, &entry->wait);}// 在等待队列(wait_queue_t)上回调函数(func)// 文件就绪后被调用,唤醒调用进程,其中key是文件提供的当前状态掩码static int pollwake(wait_queue_t *wait, unsigned mode, int sync, void *key){ struct poll_table_entry *entry; // 取得文件对应的poll_table_entry entry = container_of(wait, struct poll_table_entry, wait); // 过滤不关注的事件 if (key && !((unsigned long)key & entry->key)) { return 0; } // 唤醒 return __pollwake(wait, mode, sync, key);}static int __pollwake(wait_queue_t *wait, unsigned mode, int sync, void *key){ struct poll_wqueues *pwq = wait->private; // 将调用进程 pwq->polling_task 关联到 dummy_wait DECLARE_WAITQUEUE(dummy_wait, pwq->polling_task); smp_wmb(); pwq->triggered = 1;// 标记为已触发 // 唤醒调用进程 return default_wake_function(&dummy_wait, mode, sync, key);}// 默认的唤醒函数,poll/select 设置的回调函数会调用此函数唤醒// 直接唤醒等待队列上的线程,即将线程移到运行队列(rq)int default_wake_function(wait_queue_t *curr, unsigned mode, int wake_flags, void *key){ // 这个函数比较复杂, 这里就不具体分析了 return try_to_wake_up(curr->private, mode, wake_flags);}?
poll,select对poll_table_entry的申请和释放采用的是类似内存池的管理方式,先使用预分配的空间,预分配的空间不足时,分配一个内存页,使用内存页上的空间。
?
// 分配或使用已先前申请的 poll_table_entry,static struct poll_table_entry *poll_get_entry(struct poll_wqueues *p) { struct poll_table_page *table = p->table; if (p->inline_index < N_INLINE_POLL_ENTRIES) { return p->inline_entries + p->inline_index++; } if (!table || POLL_TABLE_FULL(table)) { struct poll_table_page *new_table; new_table = (struct poll_table_page *) __get_free_page(GFP_KERNEL); if (!new_table) { p->error = -ENOMEM; return NULL; } new_table->entry = new_table->entries; new_table->next = table; p->table = new_table; table = new_table; } return table->entry++;}// 清理poll_wqueues 占用的资源void poll_freewait(struct poll_wqueues *pwq){ struct poll_table_page * p = pwq->table; // 遍历所有已分配的inline poll_table_entry int i; for (i = 0; i < pwq->inline_index; i++) { free_poll_entry(pwq->inline_entries + i); } // 遍历在poll_table_page上分配的inline poll_table_entry // 并释放poll_table_page while (p) { struct poll_table_entry * entry; struct poll_table_page *old; entry = p->entry; do { entry--; free_poll_entry(entry); } while (entry > p->entries); old = p; p = p->next; free_page((unsigned long) old); }}static void free_poll_entry(struct poll_table_entry *entry){ // 从等待队列中删除, 释放文件引用计数 remove_wait_queue(entry->wait_address, &entry->wait); fput(entry->filp);}?
?poll/select核心结构关系下图是 poll/select 实现公共部分的关系图,包含了与文件直接的关系,以及函数之间的依赖。
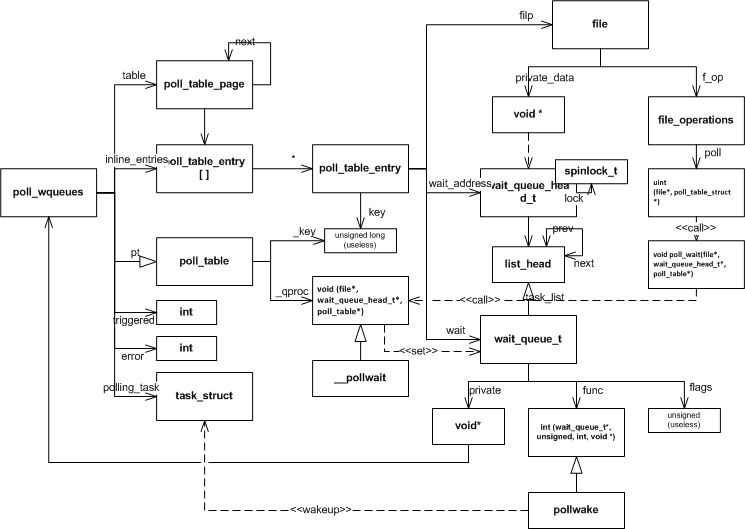
?
?poll的实现?
// poll 使用的结构体struct pollfd { int fd; // 描述符 short events; // 关注的事件掩码 short revents; // 返回的事件掩码};// long sys_poll(struct pollfd *ufds, unsigned int nfds, long timeout_msecs)SYSCALL_DEFINE3(poll, struct pollfd __user *, ufds, unsigned int, nfds, long, timeout_msecs){ struct timespec end_time, *to = NULL; int ret; if (timeout_msecs >= 0) { to = &end_time; // 将相对超时时间msec 转化为绝对时间 poll_select_set_timeout(to, timeout_msecs / MSEC_PER_SEC, NSEC_PER_MSEC * (timeout_msecs % MSEC_PER_SEC)); } // do sys poll ret = do_sys_poll(ufds, nfds, to); // do_sys_poll 被信号中断, 重新调用, 对使用者来说 poll 是不会被信号中断的. if (ret == -EINTR) { struct restart_block *restart_block; restart_block = ¤t_thread_info()->restart_block; restart_block->fn = do_restart_poll; // 设置重启的函数 restart_block->poll.ufds = ufds; restart_block->poll.nfds = nfds; if (timeout_msecs >= 0) { restart_block->poll.tv_sec = end_time.tv_sec; restart_block->poll.tv_nsec = end_time.tv_nsec; restart_block->poll.has_timeout = 1; } else { restart_block->poll.has_timeout = 0; } // ERESTART_RESTARTBLOCK 不会返回给用户进程, // 而是会被系统捕获, 然后调用 do_restart_poll, ret = -ERESTART_RESTARTBLOCK; } return ret;}int do_sys_poll(struct pollfd __user *ufds, unsigned int nfds, struct timespec *end_time){ struct poll_wqueues table; int err = -EFAULT, fdcount, len, size; /* 首先使用栈上的空间,节约内存,加速访问 */ long stack_pps[POLL_STACK_ALLOC/sizeof(long)]; struct poll_list *const head = (struct poll_list *)stack_pps; struct poll_list *walk = head; unsigned long todo = nfds; if (nfds > rlimit(RLIMIT_NOFILE)) { // 文件描述符数量超过当前进程限制 return -EINVAL; } // 复制用户空间数据到内核 len = min_t(unsigned int, nfds, N_STACK_PPS); for (;;) { walk->next = NULL; walk->len = len; if (!len) { break; } // 复制到当前的 entries if (copy_from_user(walk->entries, ufds + nfds-todo, sizeof(struct pollfd) * walk->len)) { goto out_fds; } todo -= walk->len; if (!todo) { break; } // 栈上空间不足,在堆上申请剩余部分 len = min(todo, POLLFD_PER_PAGE); size = sizeof(struct poll_list) + sizeof(struct pollfd) * len; walk = walk->next = kmalloc(size, GFP_KERNEL); if (!walk) { err = -ENOMEM; goto out_fds; } } // 初始化 poll_wqueues 结构, 设置函数指针_qproc 为__pollwait poll_initwait(&table); // poll fdcount = do_poll(nfds, head, &table, end_time); // 从文件wait queue 中移除对应的节点, 释放entry. poll_freewait(&table); // 复制结果到用户空间 for (walk = head; walk; walk = walk->next) { struct pollfd *fds = walk->entries; int j; for (j = 0; j < len; j++, ufds++) if (__put_user(fds[j].revents, &ufds->revents)) { goto out_fds; } } err = fdcount;out_fds: // 释放申请的内存 walk = head->next; while (walk) { struct poll_list *pos = walk; walk = walk->next; kfree(pos); } return err;}// 真正的处理函数static int do_poll(unsigned int nfds, struct poll_list *list, struct poll_wqueues *wait, struct timespec *end_time){ poll_table* pt = &wait->pt; ktime_t expire, *to = NULL; int timed_out = 0, count = 0; unsigned long slack = 0; if (end_time && !end_time->tv_sec && !end_time->tv_nsec) { // 已经超时,直接遍历所有文件描述符, 然后返回 pt = NULL; timed_out = 1; } if (end_time && !timed_out) { // 估计进程等待时间,纳秒 slack = select_estimate_accuracy(end_time); } // 遍历文件,为每个文件的等待队列添加唤醒函数(pollwake) for (;;) { struct poll_list *walk; for (walk = list; walk != NULL; walk = walk->next) { struct pollfd * pfd, * pfd_end; pfd = walk->entries; pfd_end = pfd + walk->len; for (; pfd != pfd_end; pfd++) { // do_pollfd 会向文件对应的wait queue 中添加节点 // 和回调函数(如果 pt 不为空) // 并检查当前文件状态并设置返回的掩码 if (do_pollfd(pfd, pt)) { // 该文件已经准备好了. // 不需要向后面文件的wait queue 中添加唤醒函数了. count++; pt = NULL; } } } // 下次循环的时候不需要向文件的wait queue 中添加节点, // 因为前面的循环已经把该添加的都添加了 pt = NULL; // 第一次遍历没有发现ready的文件 if (!count) { count = wait->error; // 有信号产生 if (signal_pending(current)) { count = -EINTR; } } // 有ready的文件或已经超时 if (count || timed_out) { break; } // 转换为内核时间 if (end_time && !to) { expire = timespec_to_ktime(*end_time); to = &expire; } // 等待事件就绪, 如果有事件发生或超时,就再循 // 环一遍,取得事件状态掩码并计数, // 注意此次循环中, 文件 wait queue 中的节点依然存在 if (!poll_schedule_timeout(wait, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, to, slack)) { timed_out = 1; } } return count;}static inline unsigned int do_pollfd(struct pollfd *pollfd, poll_table *pwait){ unsigned int mask; int fd; mask = 0; fd = pollfd->fd; if (fd >= 0) { int fput_needed; struct file * file; // 取得fd对应的文件结构体 file = fget_light(fd, &fput_needed); mask = POLLNVAL; if (file != NULL) { // 如果没有 f_op 或 f_op->poll 则认为文件始终处于就绪状态. mask = DEFAULT_POLLMASK; if (file->f_op && file->f_op->poll) { if (pwait) { // 设置关注的事件掩码 pwait->key = pollfd->events | POLLERR | POLLHUP; } // 注册回调函数,并返回当前就绪状态,就绪后会调用pollwake mask = file->f_op->poll(file, pwait); } mask &= pollfd->events | POLLERR | POLLHUP; // 移除不需要的状态掩码 fput_light(file, fput_needed);// 释放文件 } } pollfd->revents = mask; // 更新事件状态 return mask;}static long do_restart_poll(struct restart_block *restart_block){ struct pollfd __user *ufds = restart_block->poll.ufds; int nfds = restart_block->poll.nfds; struct timespec *to = NULL, end_time; int ret; if (restart_block->poll.has_timeout) { // 获取先前的超时时间 end_time.tv_sec = restart_block->poll.tv_sec; end_time.tv_nsec = restart_block->poll.tv_nsec; to = &end_time; } ret = do_sys_poll(ufds, nfds, to); // 重新调用 do_sys_poll if (ret == -EINTR) { // 又被信号中断了, 再次重启 restart_block->fn = do_restart_poll; ret = -ERESTART_RESTARTBLOCK; } return ret;}?
?
?
select 实现?
typedef struct { unsigned long *in, *out, *ex; unsigned long *res_in, *res_out, *res_ex;} fd_set_bits;// long sys_select(int n, fd_set *inp, fd_set *outp, fd_set *exp, struct timeval *tvp)SYSCALL_DEFINE5(select, int, n, fd_set __user *, inp, fd_set __user *, outp, fd_set __user *, exp, struct timeval __user *, tvp){ struct timespec end_time, *to = NULL; struct timeval tv; int ret; if (tvp) { if (copy_from_user(&tv, tvp, sizeof(tv))) { return -EFAULT; } // 计算超时时间 to = &end_time; if (poll_select_set_timeout(to, tv.tv_sec + (tv.tv_usec / USEC_PER_SEC), (tv.tv_usec % USEC_PER_SEC) * NSEC_PER_USEC)) { return -EINVAL; } } ret = core_sys_select(n, inp, outp, exp, to); // 复制剩余时间到用户空间 ret = poll_select_copy_remaining(&end_time, tvp, 1, ret); return ret;}int core_sys_select(int n, fd_set __user *inp, fd_set __user *outp, fd_set __user *exp, struct timespec *end_time){ fd_set_bits fds; void *bits; int ret, max_fds; unsigned int size; struct fdtable *fdt; //小对象使用栈上的空间,节约内存, 加快访问速度 long stack_fds[SELECT_STACK_ALLOC/sizeof(long)]; ret = -EINVAL; if (n < 0) { goto out_nofds; } rcu_read_lock(); // 取得进程对应的 fdtable fdt = files_fdtable(current->files); max_fds = fdt->max_fds; rcu_read_unlock(); if (n > max_fds) { n = max_fds; } size = FDS_BYTES(n); bits = stack_fds; if (size > sizeof(stack_fds) / 6) { // 栈上的空间不够, 申请内存, 全部使用堆上的空间 ret = -ENOMEM; bits = kmalloc(6 * size, GFP_KERNEL); if (!bits) { goto out_nofds; } } fds.in = bits; fds.out = bits + size; fds.ex = bits + 2*size; fds.res_in = bits + 3*size; fds.res_out = bits + 4*size; fds.res_ex = bits + 5*size; // 复制用户空间到内核 if ((ret = get_fd_set(n, inp, fds.in)) || (ret = get_fd_set(n, outp, fds.out)) || (ret = get_fd_set(n, exp, fds.ex))) { goto out; } // 初始化fd set zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_in); zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_out); zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_ex); ret = do_select(n, &fds, end_time); if (ret < 0) { goto out; } if (!ret) { // 该返回值会被系统捕获, 并以同样的参数重新调用sys_select() ret = -ERESTARTNOHAND; if (signal_pending(current)) { goto out; } ret = 0; } // 复制到用户空间 if (set_fd_set(n, inp, fds.res_in) || set_fd_set(n, outp, fds.res_out) || set_fd_set(n, exp, fds.res_ex)) { ret = -EFAULT; }out: if (bits != stack_fds) { kfree(bits); }out_nofds: return ret;}int do_select(int n, fd_set_bits *fds, struct timespec *end_time){ ktime_t expire, *to = NULL; struct poll_wqueues table; poll_table *wait; int retval, i, timed_out = 0; unsigned long slack = 0; rcu_read_lock(); // 检查fds中fd的有效性, 并获取当前最大的fd retval = max_select_fd(n, fds); rcu_read_unlock(); if (retval < 0) { return retval; } n = retval; // 初始化 poll_wqueues 结构, 设置函数指针_qproc为__pollwait poll_initwait(&table); wait = &table.pt; if (end_time && !end_time->tv_sec && !end_time->tv_nsec) { wait = NULL; timed_out = 1; } if (end_time && !timed_out) { // 估计需要等待的时间. slack = select_estimate_accuracy(end_time); } retval = 0; for (;;) { unsigned long *rinp, *routp, *rexp, *inp, *outp, *exp; inp = fds->in; outp = fds->out; exp = fds->ex; rinp = fds->res_in; routp = fds->res_out; rexp = fds->res_ex; // 遍历所有的描述符, i 文件描述符 for (i = 0; i < n; ++rinp, ++routp, ++rexp) { unsigned long in, out, ex, all_bits, bit = 1, mask, j; unsigned long res_in = 0, res_out = 0, res_ex = 0; const struct file_operations *f_op = NULL; struct file *file = NULL; // 检查当前的 slot 中的描述符 in = *inp++; out = *outp++; ex = *exp++; all_bits = in | out | ex; if (all_bits == 0) { // 没有需要监听的描述符, 下一个slot i += __NFDBITS; continue; } for (j = 0; j < __NFDBITS; ++j, ++i, bit <<= 1) { int fput_needed; if (i >= n) { break; } // 不需要监听描述符 i if (!(bit & all_bits)) { continue; } // 取得文件结构 file = fget_light(i, &fput_needed); if (file) { f_op = file->f_op; // 没有 f_op 的话就认为一直处于就绪状态 mask = DEFAULT_POLLMASK; if (f_op && f_op->poll) { // 设置等待事件的掩码 wait_key_set(wait, in, out, bit); /* static inline void wait_key_set(poll_table *wait, unsigned long in, unsigned long out, unsigned long bit) { wait->_key = POLLEX_SET;// (POLLPRI) if (in & bit) wait->_key |= POLLIN_SET;//(POLLRDNORM | POLLRDBAND | POLLIN | POLLHUP | POLLERR) if (out & bit) wait->_key |= POLLOUT_SET;//POLLOUT_SET (POLLWRBAND | POLLWRNORM | POLLOUT | POLLERR) } */ // 获取当前的就绪状态, 并添加到文件的对应等待队列中 mask = (*f_op->poll)(file, wait); // 和poll完全一样 } fput_light(file, fput_needed); // 释放文件 // 检查文件 i 是否已有事件就绪, if ((mask & POLLIN_SET) && (in & bit)) { res_in |= bit; retval++; // 如果已有就绪事件就不再向其他文件的 // 等待队列中添加回调函数 wait = NULL; } if ((mask & POLLOUT_SET) && (out & bit)) { res_out |= bit; retval++; wait = NULL; } if ((mask & POLLEX_SET) && (ex & bit)) { res_ex |= bit; retval++; wait = NULL; } } } if (res_in) { *rinp = res_in; } if (res_out) { *routp = res_out; } if (res_ex) { *rexp = res_ex; } cond_resched(); } wait = NULL; // 该添加回调函数的都已经添加了 if (retval || timed_out || signal_pending(current)) { break; // 信号发生,监听事件就绪或超时 } if (table.error) { retval = table.error; // 产生错误了 break; } // 转换到内核时间 if (end_time && !to) { expire = timespec_to_ktime(*end_time); to = &expire; } // 等待直到超时, 或由回调函数唤醒, 超时后会再次遍历文件描述符 if (!poll_schedule_timeout(&table, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, to, slack)) { timed_out = 1; } } poll_freewait(&table); return retval;}?
?epoll实现?
epoll 的实现比poll/select 复杂一些,这是因为:
1.? epoll_wait, epoll_ctl 的调用完全独立开来,内核需要锁机制对这些操作进行保护,并且需要持久的维护添加到epoll的文件
2.? epoll本身也是文件,也可以被poll/select/epoll监视,这可能导致epoll之间循环唤醒的问题
3.? 单个文件的状态改变可能唤醒过多监听在其上的epoll,产生唤醒风暴
epoll各个功能的实现要非常小心面对这些问题,使得复杂度大大增加。
?
epoll的核心数据结构?
// epoll的核心实现对应于一个epoll描述符struct eventpoll { spinlock_t lock; struct mutex mtx; wait_queue_head_t wq; // sys_epoll_wait() 等待在这里 // f_op->poll() 使用的, 被其他事件通知机制利用的wait_address wait_queue_head_t poll_wait; /* 已就绪的需要检查的epitem 列表 */ struct list_head rdllist; /* 保存所有加入到当前epoll的文件对应的epitem*/ struct rb_root rbr; // 当正在向用户空间复制数据时, 产生的可用文件 struct epitem *ovflist; /* The user that created the eventpoll descriptor */ struct user_struct *user; struct file *file; /*优化循环检查,避免循环检查中重复的遍历 */ int visited; struct list_head visited_list_link;}// 对应于一个加入到epoll的文件struct epitem { // 挂载到eventpoll 的红黑树节点 struct rb_node rbn; // 挂载到eventpoll.rdllist 的节点 struct list_head rdllink; // 连接到ovflist 的指针 struct epitem *next; /* 文件描述符信息fd + file, 红黑树的key */ struct epoll_filefd ffd; /* Number of active wait queue attached to poll operations */ int nwait; // 当前文件的等待队列(eppoll_entry)列表 // 同一个文件上可能会监视多种事件, // 这些事件可能属于不同的wait_queue中 // (取决于对应文件类型的实现), // 所以需要使用链表 struct list_head pwqlist; // 当前epitem 的所有者 struct eventpoll *ep; /* List header used to link this item to the "struct file" items list */ struct list_head fllink; /* epoll_ctl 传入的用户数据 */ struct epoll_event event;};struct epoll_filefd { struct file *file; int fd;};// 与一个文件上的一个wait_queue_head 相关联,因为同一文件可能有多个等待的事件,这些事件可能使用不同的等待队列struct eppoll_entry { // List struct epitem.pwqlist struct list_head llink; // 所有者 struct epitem *base; // 添加到wait_queue 中的节点 wait_queue_t wait; // 文件wait_queue 头 wait_queue_head_t *whead;};// 用户使用的epoll_eventstruct epoll_event { __u32 events; __u64 data;} EPOLL_PACKED;?
?
文件系统初始化和epoll_create?
// epoll 文件系统的相关实现// epoll 文件系统初始化, 在系统启动时会调用static int __init eventpoll_init(void){ struct sysinfo si; si_meminfo(&si); // 限制可添加到epoll的最多的描述符数量 max_user_watches = (((si.totalram - si.totalhigh) / 25) << PAGE_SHIFT) / EP_ITEM_COST; BUG_ON(max_user_watches < 0); // 初始化递归检查队列 ep_nested_calls_init(&poll_loop_ncalls); ep_nested_calls_init(&poll_safewake_ncalls); ep_nested_calls_init(&poll_readywalk_ncalls); // epoll 使用的slab分配器分别用来分配epitem和eppoll_entry epi_cache = kmem_cache_create("eventpoll_epi", sizeof(struct epitem), 0, SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN | SLAB_PANIC, NULL); pwq_cache = kmem_cache_create("eventpoll_pwq", sizeof(struct eppoll_entry), 0, SLAB_PANIC, NULL); return 0;}SYSCALL_DEFINE1(epoll_create, int, size){ if (size <= 0) { return -EINVAL; } return sys_epoll_create1(0);}SYSCALL_DEFINE1(epoll_create1, int, flags){ int error, fd; struct eventpoll *ep = NULL; struct file *file; /* Check the EPOLL_* constant for consistency.*/ BUILD_BUG_ON(EPOLL_CLOEXEC != O_CLOEXEC); if (flags & ~EPOLL_CLOEXEC) { return -EINVAL; } /* * Create the internal data structure ("struct eventpoll"). */ error = ep_alloc(&ep); if (error < 0) { return error; } /* * Creates all the items needed to setup an eventpoll file. That is, * a file structure and a free file descriptor. */ fd = get_unused_fd_flags(O_RDWR | (flags & O_CLOEXEC)); if (fd < 0) { error = fd; goto out_free_ep; } // 设置epfd的相关操作,由于epoll也是文件也提供了poll操作 file = anon_inode_getfile("[eventpoll]", &eventpoll_fops, ep, O_RDWR | (flags & O_CLOEXEC)); if (IS_ERR(file)) { error = PTR_ERR(file); goto out_free_fd; } fd_install(fd, file); ep->file = file; return fd;out_free_fd: put_unused_fd(fd);out_free_ep: ep_free(ep); return error;}?
?
?
epoll中的递归死循环和深度检查?
递归深度检测(ep_call_nested)epoll本身也是文件,也可以被poll/select/epoll监视,如果epoll之间互相监视就有可能导致死循环。epoll的实现中,所有可能产生递归调用的函数都由函函数ep_call_nested进行包裹,递归调用过程中出现死循环或递归过深就会打破死循环和递归调用直接返回。该函数的实现依赖于一个外部的全局链表nested_call_node(不同的函数调用使用不同的节点),每次调用可能发生递归的函数(nproc)就向链表中添加一个包含当前函数调用上下文ctx(进程,CPU,或epoll文件)和处理的对象标识cookie的节点,通过检测是否有相同的节点就可以知道是否发生了死循环,检查链表中同一上下文包含的节点个数就可以知道递归的深度。以下就是这一过程的源码。
struct nested_call_node { struct list_head llink; void *cookie; // 函数运行标识, 任务标志 void *ctx; // 运行环境标识};struct nested_calls { struct list_head tasks_call_list; spinlock_t lock;};// 全局的不同调用使用的链表// 死循环检查和唤醒风暴检查链表static nested_call_node poll_loop_ncalls;// 唤醒时使用的检查链表static nested_call_node poll_safewake_ncalls;// 扫描readylist 时使用的链表static nested_call_node poll_readywalk_ncalls;// 限制epoll 中直接或间接递归调用的深度并防止死循环// ctx: 任务运行上下文(进程, CPU 等)// cookie: 每个任务的标识// priv: 任务运行需要的私有数据// 如果用面向对象语言实现应该就会是一个wapper类static int ep_call_nested(struct nested_calls *ncalls, int max_nests, int (*nproc)(void *, void *, int), void *priv, void *cookie, void *ctx){ int error, call_nests = 0; unsigned long flags; struct list_head *lsthead = &ncalls->tasks_call_list; struct nested_call_node *tncur; struct nested_call_node tnode; spin_lock_irqsave(&ncalls->lock, flags); // 检查原有的嵌套调用链表ncalls, 查看是否有深度超过限制的情况 list_for_each_entry(tncur, lsthead, llink) { // 同一上下文中(ctx)有相同的任务(cookie)说明产生了死循环 // 同一上下文的递归深度call_nests 超过限制 if (tncur->ctx == ctx && (tncur->cookie == cookie || ++call_nests > max_nests)) { error = -1; } goto out_unlock; } /* 将当前的任务请求添加到调用列表*/ tnode.ctx = ctx; tnode.cookie = cookie; list_add(&tnode.llink, lsthead); spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ncalls->lock, flags); /* nproc 可能会导致递归调用(直接或间接)ep_call_nested * 如果发生递归调用, 那么在此函数返回之前, * ncalls 又会被加入额外的节点, * 这样通过前面的检测就可以知道递归调用的深度 */ error = (*nproc)(priv, cookie, call_nests); /* 从链表中删除当前任务*/ spin_lock_irqsave(&ncalls->lock, flags); list_del(&tnode.llink);out_unlock: spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ncalls->lock, flags); return error;}?
循环检测(ep_loop_check)循环检查(ep_loop_check),该函数递归调用ep_loop_check_proc利用ep_call_nested来实现epoll之间相互监视的死循环。因为ep_call_nested中已经对死循环和过深的递归做了检查,实际的ep_loop_check_proc的实现只是递归调用自己。其中的visited_list和visited标记完全是为了优化处理速度,如果没有visited_list和visited标记函数也是能够工作的。该函数中得上下文就是当前的进程,cookie就是正在遍历的epoll结构。
?
static LIST_HEAD(visited_list);// 检查 file (epoll)和ep 之间是否有循环static int ep_loop_check(struct eventpoll *ep, struct file *file){ int ret; struct eventpoll *ep_cur, *ep_next; ret = ep_call_nested(&poll_loop_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS, ep_loop_check_proc, file, ep, current); /* 清除链表和标志 */ list_for_each_entry_safe(ep_cur, ep_next, &visited_list, visited_list_link) { ep_cur->visited = 0; list_del(&ep_cur->visited_list_link); } return ret;}static int ep_loop_check_proc(void *priv, void *cookie, int call_nests){ int error = 0; struct file *file = priv; struct eventpoll *ep = file->private_data; struct eventpoll *ep_tovisit; struct rb_node *rbp; struct epitem *epi; mutex_lock_nested(&ep->mtx, call_nests + 1); // 标记当前为已遍历 ep->visited = 1; list_add(&ep->visited_list_link, &visited_list); // 遍历所有ep 监视的文件 for (rbp = rb_first(&ep->rbr); rbp; rbp = rb_next(rbp)) { epi = rb_entry(rbp, struct epitem, rbn); if (unlikely(is_file_epoll(epi->ffd.file))) { ep_tovisit = epi->ffd.file->private_data; // 跳过先前已遍历的, 避免循环检查 if (ep_tovisit->visited) { continue; } // 所有ep监视的未遍历的epoll error = ep_call_nested(&poll_loop_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS, ep_loop_check_proc, epi->ffd.file, ep_tovisit, current); if (error != 0) { break; } } else { // 文件不在tfile_check_list 中, 添加 // 最外层的epoll 需要检查子epoll监视的文件 if (list_empty(&epi->ffd.file->f_tfile_llink)) list_add(&epi->ffd.file->f_tfile_llink, &tfile_check_list); } } mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx); return error;}?
?
?
?唤醒风暴检测(reverse_path_check)?当文件状态发生改变时,会唤醒监听在其上的epoll文件,而这个epoll文件还可能唤醒其他的epoll文件,这种连续的唤醒就形成了一个唤醒路径,所有的唤醒路径就形成了一个有向图。如果文件对应的epoll唤醒有向图的节点过多,那么文件状态的改变就会唤醒所有的这些epoll(可能会唤醒很多进程,这样的开销是很大的),而实际上一个文件经过少数epoll处理以后就可能从就绪转到未就绪,剩余的epoll虽然认为文件已就绪而实际上经过某些处理后已不可用。epoll的实现中考虑到了此问题,在每次添加新文件到epoll中时,就会首先检查是否会出现这样的唤醒风暴。
该函数的实现逻辑是这样的,递归调用reverse_path_check_proc遍历监听在当前文件上的epoll文件,在reverse_pach_check_proc中统计并检查不同路径深度上epoll的个数,从而避免产生唤醒风暴。
?
#define PATH_ARR_SIZE 5// 在EPOLL_CTL_ADD 时, 检查是否有可能产生唤醒风暴// epoll 允许的单个文件的唤醒深度小于5, 例如// 一个文件最多允许唤醒1000个深度为1的epoll描述符,//允许所有被单个文件直接唤醒的epoll描述符再次唤醒的epoll描述符总数是500//// 深度限制static const int path_limits[PATH_ARR_SIZE] = { 1000, 500, 100, 50, 10 };// 计算出来的深度static int path_count[PATH_ARR_SIZE];static int path_count_inc(int nests){ /* Allow an arbitrary number of depth 1 paths */ if (nests == 0) { return 0; } if (++path_count[nests] > path_limits[nests]) { return -1; } return 0;}static void path_count_init(void){ int i; for (i = 0; i < PATH_ARR_SIZE; i++) { path_count[i] = 0; }}// 唤醒风暴检查函数static int reverse_path_check(void){ int error = 0; struct file *current_file; /* let's call this for all tfiles */ // 遍历全局tfile_check_list 中的文件, 第一级 list_for_each_entry(current_file, &tfile_check_list, f_tfile_llink) { // 初始化 path_count_init(); // 限制递归的深度, 并检查每个深度上唤醒的epoll 数量 error = ep_call_nested(&poll_loop_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS, reverse_path_check_proc, current_file, current_file, current); if (error) { break; } } return error;}static int reverse_path_check_proc(void *priv, void *cookie, int call_nests){ int error = 0; struct file *file = priv; struct file *child_file; struct epitem *epi; list_for_each_entry(epi, &file->f_ep_links, fllink) { // 遍历监视file 的epoll child_file = epi->ep->file; if (is_file_epoll(child_file)) { if (list_empty(&child_file->f_ep_links)) { // 没有其他的epoll监视当前的这个epoll, // 已经是叶子了 if (path_count_inc(call_nests)) { error = -1; break; } } else { // 遍历监视这个epoll 文件的epoll, // 递归调用 error = ep_call_nested(&poll_loop_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS, reverse_path_check_proc, child_file, child_file, current); } if (error != 0) { break; } } else { // 不是epoll , 不可能吧? printk(KERN_ERR "reverse_path_check_proc: " "file is not an ep!\n"); } } return error;}?
?epoll 的唤醒过程?
?
static void ep_poll_safewake(wait_queue_head_t *wq){ int this_cpu = get_cpu(); ep_call_nested(&poll_safewake_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS, ep_poll_wakeup_proc, NULL, wq, (void *) (long) this_cpu); put_cpu();}static int ep_poll_wakeup_proc(void *priv, void *cookie, int call_nests){ ep_wake_up_nested((wait_queue_head_t *) cookie, POLLIN, 1 + call_nests); return 0;}static inline void ep_wake_up_nested(wait_queue_head_t *wqueue, unsigned long events, int subclass){ // 这回唤醒所有正在等待此epfd 的select/epoll/poll 等 // 如果唤醒的是epoll 就可能唤醒其他的epoll, 产生连锁反应 // 这个很可能在中断上下文中被调用 wake_up_poll(wqueue, events);}?
?
?epoll_ctl?// long epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_ctl, int, epfd, int, op, int, fd, struct epoll_event __user *, event){ int error; int did_lock_epmutex = 0; struct file *file, *tfile; struct eventpoll *ep; struct epitem *epi; struct epoll_event epds; error = -EFAULT; if (ep_op_has_event(op) && // 复制用户空间数据到内核 copy_from_user(&epds, event, sizeof(struct epoll_event))) { goto error_return; } // 取得 epfd 对应的文件 error = -EBADF; file = fget(epfd); if (!file) { goto error_return; } // 取得目标文件 tfile = fget(fd); if (!tfile) { goto error_fput; } // 目标文件必须提供 poll 操作 error = -EPERM; if (!tfile->f_op || !tfile->f_op->poll) { goto error_tgt_fput; } // 添加自身或epfd 不是epoll 句柄 error = -EINVAL; if (file == tfile || !is_file_epoll(file)) { goto error_tgt_fput; } // 取得内部结构eventpoll ep = file->private_data; // EPOLL_CTL_MOD 不需要加全局锁 epmutex if (op == EPOLL_CTL_ADD || op == EPOLL_CTL_DEL) { mutex_lock(&epmutex); did_lock_epmutex = 1; } if (op == EPOLL_CTL_ADD) { if (is_file_epoll(tfile)) { error = -ELOOP; // 目标文件也是epoll 检测是否有循环包含的问题 if (ep_loop_check(ep, tfile) != 0) { goto error_tgt_fput; } } else { // 将目标文件添加到 epoll 全局的tfile_check_list 中 list_add(&tfile->f_tfile_llink, &tfile_check_list); } } mutex_lock_nested(&ep->mtx, 0); // 以tfile 和fd 为key 在rbtree 中查找文件对应的epitem epi = ep_find(ep, tfile, fd); error = -EINVAL; switch (op) { case EPOLL_CTL_ADD: if (!epi) { // 没找到, 添加额外添加ERR HUP 事件 epds.events |= POLLERR | POLLHUP; error = ep_insert(ep, &epds, tfile, fd); } else { error = -EEXIST; } // 清空文件检查列表 clear_tfile_check_list(); break; case EPOLL_CTL_DEL: if (epi) { error = ep_remove(ep, epi); } else { error = -ENOENT; } break; case EPOLL_CTL_MOD: if (epi) { epds.events |= POLLERR | POLLHUP; error = ep_modify(ep, epi, &epds); } else { error = -ENOENT; } break; } mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);error_tgt_fput: if (did_lock_epmutex) { mutex_unlock(&epmutex); } fput(tfile);error_fput: fput(file);error_return: return error;}?
?
EPOLL_CTL_ADD 实现?
// EPOLL_CTL_ADDstatic int ep_insert(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event *event, struct file *tfile, int fd){ int error, revents, pwake = 0; unsigned long flags; long user_watches; struct epitem *epi; struct ep_pqueue epq; /* struct ep_pqueue { poll_table pt; struct epitem *epi; }; */ // 增加监视文件数 user_watches = atomic_long_read(&ep->user->epoll_watches); if (unlikely(user_watches >= max_user_watches)) { return -ENOSPC; } // 分配初始化 epi if (!(epi = kmem_cache_alloc(epi_cache, GFP_KERNEL))) { return -ENOMEM; } INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->rdllink); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->fllink); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->pwqlist); epi->ep = ep; // 初始化红黑树中的key ep_set_ffd(&epi->ffd, tfile, fd); // 直接复制用户结构 epi->event = *event; epi->nwait = 0; epi->next = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR; // 初始化临时的 epq epq.epi = epi; init_poll_funcptr(&epq.pt, ep_ptable_queue_proc);// 设置事件掩码 epq.pt._key = event->events; // 内部会调用ep_ptable_queue_proc, 在文件对应的wait queue head 上 // 注册回调函数, 并返回当前文件的状态 revents = tfile->f_op->poll(tfile, &epq.pt); // 检查错误 error = -ENOMEM; if (epi->nwait < 0) { // f_op->poll 过程出错 goto error_unregister; } // 添加当前的epitem 到文件的f_ep_links 链表 spin_lock(&tfile->f_lock); list_add_tail(&epi->fllink, &tfile->f_ep_links); spin_unlock(&tfile->f_lock); // 插入epi 到rbtree ep_rbtree_insert(ep, epi); /* now check if we've created too many backpaths */ error = -EINVAL; if (reverse_path_check()) { goto error_remove_epi; } spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags); /* 文件已经就绪插入到就绪链表rdllist */ if ((revents & event->events) && !ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) { list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist); if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq)) // 通知sys_epoll_wait , 调用回调函数唤醒sys_epoll_wait 进程 { wake_up_locked(&ep->wq); } // 先不通知调用eventpoll_poll 的进程 if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait)) { pwake++; } } spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags); atomic_long_inc(&ep->user->epoll_watches); if (pwake) // 安全通知调用eventpoll_poll 的进程 { ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait); } return 0;error_remove_epi: spin_lock(&tfile->f_lock); // 删除文件上的 epi if (ep_is_linked(&epi->fllink)) { list_del_init(&epi->fllink); } spin_unlock(&tfile->f_lock); // 从红黑树中删除 rb_erase(&epi->rbn, &ep->rbr);error_unregister: // 从文件的wait_queue 中删除, 释放epitem 关联的所有eppoll_entry ep_unregister_pollwait(ep, epi); /* * We need to do this because an event could have been arrived on some * allocated wait queue. Note that we don't care about the ep->ovflist * list, since that is used/cleaned only inside a section bound by "mtx". * And ep_insert() is called with "mtx" held. */ // TODO: spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags); if (ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) { list_del_init(&epi->rdllink); } spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags); // 释放epi kmem_cache_free(epi_cache, epi); return error;}?
?EPOLL_CTL_DELEPOLL_CTL_DEL 的实现调用的是 ep_remove 函数,函数只是清除ADD时, 添加的各种结构,EPOLL_CTL_MOD 的实现调用的是ep_modify,在ep_modify中用新的事件掩码调用f_ops->poll,检测事件是否已可用,如果可用就直接唤醒epoll,这两个的实现与EPOLL_CTL_ADD 类似,代码上比较清晰,这里就不具体分析了。
?
?
static int ep_remove(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epitem *epi){unsigned long flags;struct file *file = epi->ffd.file;/* * Removes poll wait queue hooks. We _have_ to do this without holding * the "ep->lock" otherwise a deadlock might occur. This because of the * sequence of the lock acquisition. Here we do "ep->lock" then the wait * queue head lock when unregistering the wait queue. The wakeup callback * will run by holding the wait queue head lock and will call our callback * that will try to get "ep->lock". */ep_unregister_pollwait(ep, epi);/* Remove the current item from the list of epoll hooks */spin_lock(&file->f_lock);if (ep_is_linked(&epi->fllink))list_del_init(&epi->fllink);spin_unlock(&file->f_lock);rb_erase(&epi->rbn, &ep->rbr);spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);if (ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink))list_del_init(&epi->rdllink);spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);/* At this point it is safe to free the eventpoll item */kmem_cache_free(epi_cache, epi);atomic_long_dec(&ep->user->epoll_watches);return 0;}??
?
?
?
/* * Modify the interest event mask by dropping an event if the new mask * has a match in the current file status. Must be called with "mtx" held. */static int ep_modify(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epitem *epi, struct epoll_event *event){int pwake = 0;unsigned int revents;poll_table pt;init_poll_funcptr(&pt, NULL);/* * Set the new event interest mask before calling f_op->poll(); * otherwise we might miss an event that happens between the * f_op->poll() call and the new event set registering. */epi->event.events = event->events;pt._key = event->events;epi->event.data = event->data; /* protected by mtx *//* * Get current event bits. We can safely use the file* here because * its usage count has been increased by the caller of this function. */revents = epi->ffd.file->f_op->poll(epi->ffd.file, &pt);/* * If the item is "hot" and it is not registered inside the ready * list, push it inside. */if (revents & event->events) {spin_lock_irq(&ep->lock);if (!ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) {list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);/* Notify waiting tasks that events are available */if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))pwake++;}spin_unlock_irq(&ep->lock);}/* We have to call this outside the lock */if (pwake)ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait);return 0;}??
?
?
epoll_wait?
?
/*epoll_wait实现*/SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_wait, int, epfd, struct epoll_event __user *, events, int, maxevents, int, timeout){ int error; struct file *file; struct eventpoll *ep; // 检查输入数据有效性 if (maxevents <= 0 || maxevents > EP_MAX_EVENTS) { return -EINVAL; } if (!access_ok(VERIFY_WRITE, events, maxevents * sizeof(struct epoll_event))) { error = -EFAULT; goto error_return; } /* Get the "struct file *" for the eventpoll file */ error = -EBADF; file = fget(epfd); if (!file) { goto error_return; } error = -EINVAL; if (!is_file_epoll(file)) { goto error_fput; } // 取得ep 结构 ep = file->private_data; // 等待事件 error = ep_poll(ep, events, maxevents, timeout);error_fput: fput(file);error_return: return error;}static int ep_poll(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event __user *events, int maxevents, long timeout){ int res = 0, eavail, timed_out = 0; unsigned long flags; long slack = 0; wait_queue_t wait; ktime_t expires, *to = NULL; if (timeout > 0) {// 转换为内核时间 struct timespec end_time = ep_set_mstimeout(timeout); slack = select_estimate_accuracy(&end_time); to = &expires; *to = timespec_to_ktime(end_time); } else if (timeout == 0) { // 已经超时直接检查readylist timed_out = 1; spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags); goto check_events; }fetch_events: spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags); // 没有可用的事件,ready list 和ovflist 都为空 if (!ep_events_available(ep)) { // 添加当前进程的唤醒函数 init_waitqueue_entry(&wait, current); __add_wait_queue_exclusive(&ep->wq, &wait); for (;;) { /* * We don't want to sleep if the ep_poll_callback() sends us * a wakeup in between. That's why we set the task state * to TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE before doing the checks. */ set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE); if (ep_events_available(ep) || timed_out) { break; } if (signal_pending(current)) { res = -EINTR; break; } spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);// 挂起当前进程,等待唤醒或超时 if (!schedule_hrtimeout_range(to, slack, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS)) { timed_out = 1; } spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags); } __remove_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait); set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING); }check_events: // 再次检查是否有可用事件 eavail = ep_events_available(ep); spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags); /* * Try to transfer events to user space. In case we get 0 events and * there's still timeout left over, we go trying again in search of * more luck. */ if (!res && eavail && !(res = ep_send_events(ep, events, maxevents)) // 复制事件到用户空间 && !timed_out) // 复制事件失败并且没有超时,重新等待。 { goto fetch_events; } return res;}static inline int ep_events_available(struct eventpoll *ep){ return !list_empty(&ep->rdllist) || ep->ovflist != EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;}struct ep_send_events_data { int maxevents; struct epoll_event __user *events;};static int ep_send_events(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event __user *events, int maxevents){ struct ep_send_events_data esed; esed.maxevents = maxevents; esed.events = events; return ep_scan_ready_list(ep, ep_send_events_proc, &esed, 0);}static int ep_send_events_proc(struct eventpoll *ep, struct list_head *head, void *priv){ struct ep_send_events_data *esed = priv; int eventcnt; unsigned int revents; struct epitem *epi; struct epoll_event __user *uevent; // 遍历已就绪链表 for (eventcnt = 0, uevent = esed->events; !list_empty(head) && eventcnt < esed->maxevents;) { epi = list_first_entry(head, struct epitem, rdllink); list_del_init(&epi->rdllink); // 获取ready 事件掩码 revents = epi->ffd.file->f_op->poll(epi->ffd.file, NULL) & epi->event.events; /* * If the event mask intersect the caller-requested one, * deliver the event to userspace. Again, ep_scan_ready_list() * is holding "mtx", so no operations coming from userspace * can change the item. */ if (revents) { // 事件就绪, 复制到用户空间 if (__put_user(revents, &uevent->events) || __put_user(epi->event.data, &uevent->data)) { list_add(&epi->rdllink, head); return eventcnt ? eventcnt : -EFAULT; } eventcnt++; uevent++; if (epi->event.events & EPOLLONESHOT) { epi->event.events &= EP_PRIVATE_BITS; } else if (!(epi->event.events & EPOLLET)) { // 不是边缘模式, 再次添加到ready list, // 下次epoll_wait 时直接进入此函数检查ready list是否仍然继续 list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist); } // 如果是边缘模式, 只有当文件状态发生改变时, // 才文件会再次触发wait_address 上wait_queue的回调函数, } } return eventcnt;}?
?
?
?
eventpoll_poll?由于epoll自身也是文件系统,其描述符也可以被poll/select/epoll监视,因此需要实现poll方法。
static const struct file_operations eventpoll_fops = { .release = ep_eventpoll_release, .poll = ep_eventpoll_poll, .llseek = noop_llseek,};static unsigned int ep_eventpoll_poll(struct file *file, poll_table *wait){ int pollflags; struct eventpoll *ep = file->private_data; // 插入到wait_queue poll_wait(file, &ep->poll_wait, wait); // 扫描就绪的文件列表, 调用每个文件上的poll 检测是否真的就绪, // 然后复制到用户空间 // 文件列表中有可能有epoll文件, 调用poll的时候有可能会产生递归, // 调用所以用ep_call_nested 包装一下, 防止死循环和过深的调用 pollflags = ep_call_nested(&poll_readywalk_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS, ep_poll_readyevents_proc, ep, ep, current); // static struct nested_calls poll_readywalk_ncalls; return pollflags != -1 ? pollflags : 0;}static int ep_poll_readyevents_proc(void *priv, void *cookie, int call_nests){ return ep_scan_ready_list(priv, ep_read_events_proc, NULL, call_nests + 1);}static int ep_scan_ready_list(struct eventpoll *ep, int (*sproc)(struct eventpoll *, struct list_head *, void *), void *priv, int depth){ int error, pwake = 0; unsigned long flags; struct epitem *epi, *nepi; LIST_HEAD(txlist); /* * We need to lock this because we could be hit by * eventpoll_release_file() and epoll_ctl(). */ mutex_lock_nested(&ep->mtx, depth); spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags); // 移动rdllist 到新的链表txlist list_splice_init(&ep->rdllist, &txlist); // 改变ovflist 的状态, 如果ep->ovflist != EP_UNACTIVE_PTR, // 当文件激活wait_queue时,就会将对应的epitem加入到ep->ovflist // 否则将文件直接加入到ep->rdllist, // 这样做的目的是避免丢失事件 // 这里不需要检查ep->ovflist 的状态,因为ep->mtx的存在保证此处的ep->ovflist // 一定是EP_UNACTIVE_PTR ep->ovflist = NULL; spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags); // 调用扫描函数处理txlist error = (*sproc)(ep, &txlist, priv); spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags); // 调用 sproc 时可能有新的事件,遍历这些新的事件将其插入到ready list for (nepi = ep->ovflist; (epi = nepi) != NULL; nepi = epi->next, epi->next = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR) { // #define EP_UNACTIVE_PTR (void *) -1 // epi 不在rdllist, 插入 if (!ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) { list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist); } } // 还原ep->ovflist的状态 ep->ovflist = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR; // 将处理后的 txlist 链接到 rdllist list_splice(&txlist, &ep->rdllist); if (!list_empty(&ep->rdllist)) { // 唤醒epoll_wait if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq)) { wake_up_locked(&ep->wq); } // 当前的ep有其他的事件通知机制监控 if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait)) { pwake++; } } spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags); mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx); if (pwake) { // 安全唤醒外部的事件通知机制 ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait); } return error;}static int ep_read_events_proc(struct eventpoll *ep, struct list_head *head, void *priv){ struct epitem *epi, *tmp; poll_table pt; init_poll_funcptr(&pt, NULL); list_for_each_entry_safe(epi, tmp, head, rdllink) { pt._key = epi->event.events; if (epi->ffd.file->f_op->poll(epi->ffd.file, &pt) & epi->event.events) { return POLLIN | POLLRDNORM; } else { // 这个事件虽然在就绪列表中, // 但是实际上并没有就绪, 将他移除 // 这有可能是水平触发模式中没有将文件从就绪列表中移除 // 也可能是事件插入到就绪列表后有其他的线程对文件进行了操作 list_del_init(&epi->rdllink); } } return 0;}?
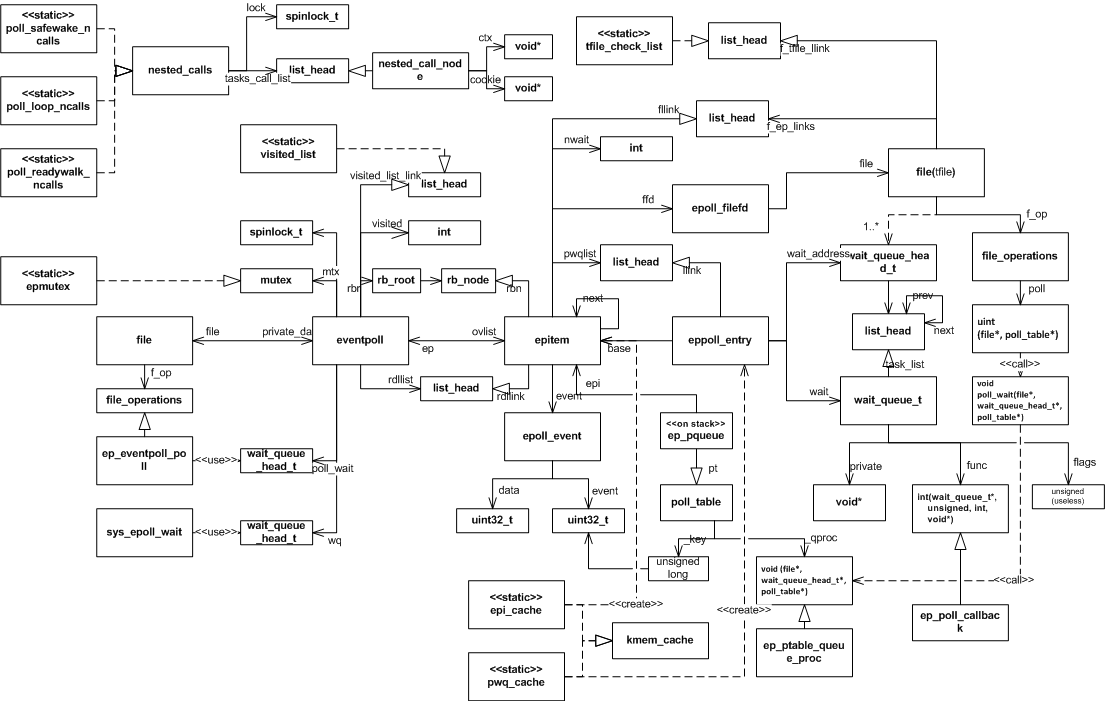
?epoll全景以下是epoll使用的全部数据结构之间的关系图,采用的是一种类UML图,希望对理解epoll的内部实现有所帮助。
?
?
?
?
?
?
?poll/select/epoll 对比通过以上的分析可以看出,poll和select的实现基本是一致,只是用户到内核传递的数据格式有所不同,
?
?
select和poll即使只有一个描述符就绪,也要遍历整个集合。如果集合中活跃的描述符很少,遍历过程的开销就会变得很大,而如果集合中大部分的描述符都是活跃的,遍历过程的开销又可以忽略。
epoll的实现中每次只遍历活跃的描述符(如果是水平触发,也会遍历先前活跃的描述符),在活跃描述符较少的情况下就会很有优势,在代码的分析过程中可以看到epoll的实现过于复杂并且其实现过程中需要同步处理(锁),如果大部分描述符都是活跃的,epoll的效率可能不如select或poll。(参见epoll 和poll的性能测试?http://jacquesmattheij.com/Poll+vs+Epoll+once+again)
select能够处理的最大fd无法超出FDSETSIZE。
select会复写传入的fd_set 指针,而poll对每个fd返回一个掩码,不更改原来的掩码,从而可以对同一个集合多次调用poll,而无需调整。
select对每个文件描述符最多使用3个bit,而poll采用的pollfd需要使用64个bit,epoll采用的 epoll_event则需要96个bit
如果事件需要循环处理select, poll 每一次的处理都要将全部的数据复制到内核,而epoll的实现中,内核将持久维护加入的描述符,减少了内核和用户复制数据的开销。
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?