C++中的重载、覆盖和隐藏的区分
今天看书遇到了C++中比较难缠的概念,就是重载、覆盖和隐藏。如果只要区分重载和覆盖,相信应该没有什么难度,并且它们的界限还是比较清晰的。现在加上了隐藏,初次看这些概念还真是不好区分。下面总结一下它们之间的区别:
成员函数的重载的特征有以下4点:
(1) 必需在相同的范围内,即在同一个类的内部;
(2) 函数名称相同;
(3) 函数的参数不相同;
(4) virtual关键字可选,即可以加上也可以不加上,不影响重载的发生。
覆盖是指派生类函数覆盖基类函数,它的特征有以下4点:
(1)必需在不同的范围中,即分别在派生类和基类中;
(2) 函数名称相同;
(3) 参数也必需相同;
(4) 基类函数必需有virtual关键字。
而隐藏行为则必需符合以下两条规则:
(1) 如果派生类的函数与基类的函数的名称相同,但是参数不同。此时,不管有无virtual关键字,基类的函数都会被派生类的同名函数隐藏;
(2) 如果派生类的函数与基类的函数同名,并且参数也相同,但是基类函数没有virtual关键字。这个时候基类的同名函数也会被隐藏。
下面Demo说明了覆盖和隐藏之间的区别
覆盖例子:
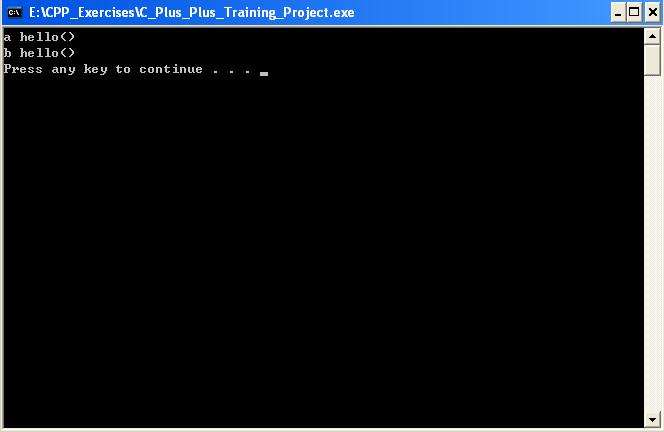
#include <iostream>#include <cstdlib>using namespace std;class a{ public : void virtual hello() { cout<<"a hello()"<<endl; } void hello(int i) { cout<<"a.hello(i)"<<i<<endl; } };class b: public a{ public: void hello() { cout<<"b hello()"<<endl; } void hello(int i) const { cout<<"b.hello(i)"<<i<<endl; } };int main(int argc,char * args[]){ { a *aptr=new b; aptr->hello(); b* bptr=new b; bptr->hello(); delete aptr; delete bptr; } system("pause"); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }上面的例子是覆盖,由于基类a中和派生类b中的hello函数的签名完全相同,而且基类a中有virtual关键字,所以基类a中的hello函数被派生类b中的hello函数所覆盖,因此具有多态的特性(只有覆盖才具有多态的特征)。
这段代码显示的结果为:
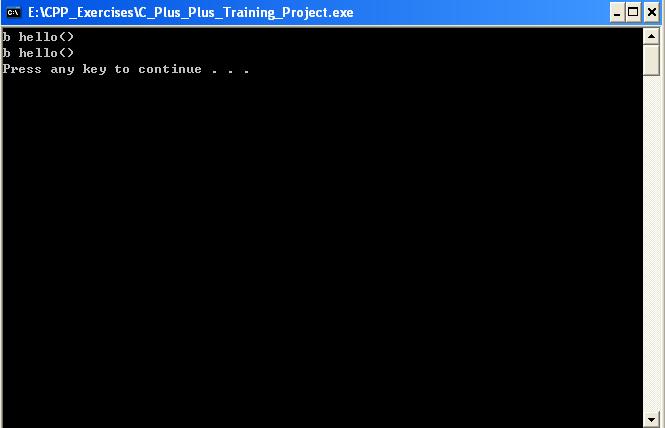
稍微改动上述代码,得到下面的例子:
#include <iostream>#include <cstdlib>using namespace std;class a{ public : void hello() { cout<<"a hello()"<<endl; } void hello(int i) { cout<<"a.hello(i)"<<i<<endl; } };class b: public a{ public: void hello() const { cout<<"b hello()"<<endl; } void hello(int i) const { cout<<"b.hello(i)"<<i<<endl; } };int main(int argc,char * args[]){ { a *aptr=new b; aptr->hello(); b* bptr=new b; bptr->hello(); delete aptr; delete bptr; } system("pause"); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }改动后代码运行的结果是: