C 算法精介----链表
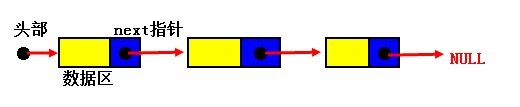
C算法 ---链表 链表是一种最为基础的数据结构,链表是由一组元素以一种特定的顺序组合或链接在一起的。在维护数据的集合时很有用途。在平时的数据处理过程中经常会会用链接进行数据的临时存储。但是如何才能使链表处理数据更加优化,下面简单介绍单链表处理情况! 1 、单链表介绍 单链表是各个元素之间通过一个指针彼此连接起来而组成的。元素可以分为2个部分:数据成员和一个称为nest的指针。通过这种2成员结构,将每个元素的next指针指向其元素后面的指针。为了更能描述这种结构可以看下图:
#ifndef LIST_H#define LIST_H#include <stdlib.h>/*define a structure for linked List elements */typedef struct ListElmt_{ void *data; struct ListElmt_ *next;}ListElmt;/*define a structure for linked lists */typedef struct List_ { int size; int (*match)(const void * key1, const void * key2); void (*destroy)(void *data); ListElmt *head; ListElmt *tail;}List;/*Public Intefaces */void list_init(List *list, void (*destroy)(void *data));void list_destory(List *list);int list_ins_next(List *list, ListElmt *element, const void *data);int list_rem_next(List *list, ListElmt *element, void *data);#define list_size(list) ((list) -> size)#define list_head(list) ((list) -> head)#define list_tail(list) ((list) -> tail)#define list_is_head(list, element) ((element) == (list) -> head ? 1:0)#define list_is_tail(list, element) ((element) == (list) -> tail ? 1:0)#define list_data(element) ((element) -> data)#define list_next(element) ((element) -> next)#endif示例2 链表抽象数据类型的实现#include <studio.h>#include <string.h>#include "../include/List.h"/*list_init */void list_init(List * list, void(* destroy)(void * data)) { /* initialize the list */ list -> size = 0; list -> destroy = destroy; list -> head = NULL; list -> tail = NULL; return ;}/*list_destroy */void list_destory(List * list) { void *data; /*Remove eah element */ while (list_size(list) > 0){ if (list_rem_next(list, NULL, (void **) &data) == 0 && list -> destroy != NULL){ /* Call a user-defined function to free dynamically allocated data*/ list -> destroy(data); } } memset(list, 0, sizeof(List)); return;}/*list_ins_nest */int list_ins_next (List * list, ListElmt * element, const void * data){ ListElmt *new_element; /* Allocate storage for the element */ if ((new_element = (ListElmt *)malloc(sizeof(ListElmt))) == NULL){ return -1; } /*insert the element into the list */ new_element ->data =(void *)data; if (element == NULL){ /* handle insertion at the head of the list */ if (list_size(list) == 0){ list -> tail = new_element; } new_element ->next = list ->head; list -> head = new_element; } else { /*Handle insertion somewhere other than at the head */ if (element ->next == NULL ){ list ->tail = new_element; } new_element ->next = element ->next; element->next = new_element; } list->size ++; return 0; }/* list_rem_next */int list_rem_next(List * list, ListElmt * element, void * data) { ListElmt *old_element; /* Do not allow removal from an emptry list */ if (list_size(list) == 0){ return -1; } /* romove the element from the list */ if (element == NULL){ /* handle removel from the head of the list */ *data = list->head->data; old_element = list ->head; list->head = list -> head->next; if (list_size(list) == 1){ list->tail = NULL; } } else { /* handle removal from somewhere other than the head */ if ( element->next == NULL){ return -1; } *data = element->next->data; old_element = element->next; element->next = element->next->next; if (element ->next == NULL){ list->tail = NULL; } } /* free the storage allocated by the abstract datatype*/ free(old_element); list->size --; return 0;}
3 下面对几个重要的函数接口实现进行介绍 list_init list_init用来初始化一个链表仪表能够执行其他的操作,主要成员的描述: size:链表中元素的个数;初始化为0; destroy:定义的一个析构函数(http://baike.baidu.com/view/1277985.htm);初始换有函数参数传入; head和tail:2个指针主要表头和表尾。初始化为NULL;list_destroy list_destroy 用来销毁链表,也就是取出链表中的所有函数; 函数主要是循环判断size,直到size为0时退出。函数的实现是调用函数list_rem_next,第二个参数为NULL时,表示,从第一个元素开始删除。如果析构函数不为NULL,则应该调用析构函数。list_ins_next list_ins_next 将一个元素插入有element指定的元素之后。新元素的数据只想由用户传入的数据。想链表中插入数据要有2中情况要考虑:插入头或其他位置,具体参照函数的实现。当传入参数element为NULL,表示从插入到表头;list_rem_next list_rem_next 从链表中移除指定元素之后的那个节点,并将其保存的数据保存的参数data中;同样也需要考虑2中情况:删除头或者其他位置的。当参数element为NULL时,表示从表头删除!4 双向链表 双向链表
list_init用来初始化一个链表仪表能够执行其他的操作,主要成员的描述: size:链表中元素的个数;初始化为0; destroy:定义的一个析构函数(http://baike.baidu.com/view/1277985.htm);初始换有函数参数传入; head和tail:2个指针主要表头和表尾。初始化为NULL;list_destroy list_destroy 用来销毁链表,也就是取出链表中的所有函数; 函数主要是循环判断size,直到size为0时退出。函数的实现是调用函数list_rem_next,第二个参数为NULL时,表示,从第一个元素开始删除。如果析构函数不为NULL,则应该调用析构函数。list_ins_next list_ins_next 将一个元素插入有element指定的元素之后。新元素的数据只想由用户传入的数据。想链表中插入数据要有2中情况要考虑:插入头或其他位置,具体参照函数的实现。当传入参数element为NULL,表示从插入到表头;list_rem_next list_rem_next 从链表中移除指定元素之后的那个节点,并将其保存的数据保存的参数data中;同样也需要考虑2中情况:删除头或者其他位置的。当参数element为NULL时,表示从表头删除!4 双向链表 双向链表
destroy:定义的一个析构函数(http://baike.baidu.com/view/1277985.htm);初始换有函数参数传入; head和tail:2个指针主要表头和表尾。初始化为NULL;list_destroy list_destroy 用来销毁链表,也就是取出链表中的所有函数; 函数主要是循环判断size,直到size为0时退出。函数的实现是调用函数list_rem_next,第二个参数为NULL时,表示,从第一个元素开始删除。如果析构函数不为NULL,则应该调用析构函数。list_ins_next list_ins_next 将一个元素插入有element指定的元素之后。新元素的数据只想由用户传入的数据。想链表中插入数据要有2中情况要考虑:插入头或其他位置,具体参照函数的实现。当传入参数element为NULL,表示从插入到表头;list_rem_next list_rem_next 从链表中移除指定元素之后的那个节点,并将其保存的数据保存的参数data中;同样也需要考虑2中情况:删除头或者其他位置的。当参数element为NULL时,表示从表头删除!4 双向链表 双向链表
list_destroy list_destroy 用来销毁链表,也就是取出链表中的所有函数; 函数主要是循环判断size,直到size为0时退出。函数的实现是调用函数list_rem_next,第二个参数为NULL时,表示,从第一个元素开始删除。如果析构函数不为NULL,则应该调用析构函数。list_ins_next list_ins_next 将一个元素插入有element指定的元素之后。新元素的数据只想由用户传入的数据。想链表中插入数据要有2中情况要考虑:插入头或其他位置,具体参照函数的实现。当传入参数element为NULL,表示从插入到表头;list_rem_next list_rem_next 从链表中移除指定元素之后的那个节点,并将其保存的数据保存的参数data中;同样也需要考虑2中情况:删除头或者其他位置的。当参数element为NULL时,表示从表头删除!4 双向链表 双向链表
函数主要是循环判断size,直到size为0时退出。函数的实现是调用函数list_rem_next,第二个参数为NULL时,表示,从第一个元素开始删除。如果析构函数不为NULL,则应该调用析构函数。list_ins_next list_ins_next 将一个元素插入有element指定的元素之后。新元素的数据只想由用户传入的数据。想链表中插入数据要有2中情况要考虑:插入头或其他位置,具体参照函数的实现。当传入参数element为NULL,表示从插入到表头;list_rem_next list_rem_next 从链表中移除指定元素之后的那个节点,并将其保存的数据保存的参数data中;同样也需要考虑2中情况:删除头或者其他位置的。当参数element为NULL时,表示从表头删除!4 双向链表 双向链表
list_ins_next 将一个元素插入有element指定的元素之后。新元素的数据只想由用户传入的数据。想链表中插入数据要有2中情况要考虑:插入头或其他位置,具体参照函数的实现。当传入参数element为NULL,表示从插入到表头;list_rem_next list_rem_next 从链表中移除指定元素之后的那个节点,并将其保存的数据保存的参数data中;同样也需要考虑2中情况:删除头或者其他位置的。当参数element为NULL时,表示从表头删除!4 双向链表 双向链表
list_rem_next 从链表中移除指定元素之后的那个节点,并将其保存的数据保存的参数data中;同样也需要考虑2中情况:删除头或者其他位置的。当参数element为NULL时,表示从表头删除!4 双向链表 双向链表
双向链表