异步I/O处理
异步I/O处理过程
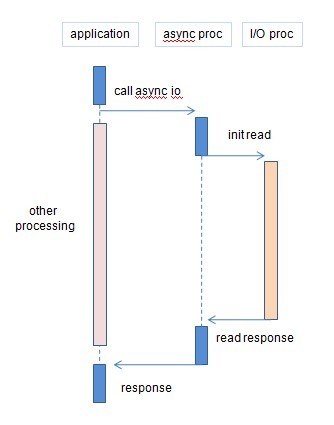
?
异步I/O处理的优点??? I/O密集型计算(进程所执行的I/O操作比执行的处理操作更多)的任务中,使用异步I/O的方式,可以提高CPU对应用程序处理的吞吐率,应用程序无需进行I/O阻塞。保证在I/O处理时,仍能进行应用程序的处理
?
?
异步I/O的缺点??? 如果程序的I/O操作频繁并且短暂,则I/O线程切换代价较大,并且异步I/O库处理有一定的开销(磁盘磁头的寻址切换等),异步I/O对程序的写法有一定的门槛。
?
异步I/O的应用场景??? NodeJS的单进程,单线程模型。为了能同时处理更多的请求,I/O操作,必需使用异步处理的方式,NodeJS采用的是libeio的实现方式。
?
异步I/O的实现glibc:在文件目录下新建file.txt文件,file.txt内容:hello world!
#include <aio.h>#include <errno.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>char bufferAO[8192] __attribute__((aligned(4096)));void aio_completion_handler(int signo, siginfo_t *info, void *context){int ret; write(1, "callback\n", 9);struct aiocb *req;// Ensure it's our signal if (info->si_signo == SIGIO) {req = (struct aiocb *)info->si_value.sival_ptr;printf("data: %s\n" ,req->aio_buf);// Did the request complete?if (aio_error( req ) == 0) {// Request completed successfully, get the return statusret = aio_return( req );}} return;}int main(){int fd, ret;struct sigaction sig_act;struct aiocb my_aiocb;fd = open("file.txt", O_RDONLY);if(fd < 0){perror("open fail");}// Set up the signal handlersigemptyset(&sig_act.sa_mask);sig_act.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO;sig_act.sa_sigaction = aio_completion_handler;// Set up the AIO requestbzero( (char *)&my_aiocb, sizeof(struct aiocb) );my_aiocb.aio_fildes = fd;my_aiocb.aio_buf = malloc(sizeof(bufferAO)+1);my_aiocb.aio_nbytes = sizeof(bufferAO);my_aiocb.aio_offset = 0;// Link the AIO request with the Signal Handlermy_aiocb.aio_sigevent.sigev_notify = SIGEV_SIGNAL;my_aiocb.aio_sigevent.sigev_signo = SIGIO;my_aiocb.aio_sigevent.sigev_value.sival_ptr = &my_aiocb;// Map the Signal to the Signal Handlerret = sigaction( SIGIO, &sig_act, NULL );ret = aio_read(&my_aiocb);if (ret < 0) {perror("error info");}write(1, "caller thread\n", 14);sleep(5);}compile:? gcc aio_demo.c -o aio_demo.o -lrt
run: ./aio_demo.o
result:
caller thread
callback
data: hello world!
?
kernel native aio:待完善
?
libeio:libeio的源码下载:https://github.com/scunningham/libeio
libeio的编译及运行过程:
./autogen.sh./configuremakesudo make installexport LD_LIBRARY_PATH=".libs;$LD_LIBRARY_PATH"#此时可以编译运行demo.c了gcc demo.c -o demo -leio./demo
?
运行结果:
?
?
具体的libeio源码及流程分析可以查看大牛已经做的文档:
NodeJS代码阅读笔记之libeio
libeio异步I/O初探
Java:Server端:
package org.operamasks.nio;import java.io.IOException;import java.net.InetSocketAddress;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;import java.nio.channels.Selector;import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;import java.nio.charset.Charset;import java.util.Calendar;import java.util.Iterator;public class TestServer {public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(new EchoServer(1982)).start();}}class EchoServer implements Runnable {//要监听的端口号private int port;//生成一个信号监视器private Selector s;//读缓冲区private ByteBuffer r_bBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);private ByteBuffer w_bBuf;public EchoServer(int port) {this.port = port;try {s = Selector.open();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public void run() {try {//生成一个ServerScoket通道的实例对象,用于侦听可能发生的IO事件ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();//将该通道设置为异步方式ssc.configureBlocking(false);//绑定到一个指定的端口ssc.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));//注册特定类型的事件到信号监视器上ssc.register(s, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);System.out.println("The server has been launched...");while(true) {//将会阻塞执行,直到有事件发生s.select();Iterator<SelectionKey> it = s.selectedKeys().iterator();while(it.hasNext()) {SelectionKey key = it.next();//key定义了四种不同形式的操作switch(key.readyOps()) {case SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT :dealwithAccept(key);break;case SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT :break;case SelectionKey.OP_READ :dealwithRead(key);break;case SelectionKey.OP_WRITE :break;}//处理结束后移除当前事件,以免重复处理it.remove();}}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//处理接收连接的事件private void dealwithAccept(SelectionKey key) {try {System.out.println("新的客户端请求连接...");ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel)key.channel();SocketChannel sc = server.accept();sc.configureBlocking(false);//注册读事件sc.register(s, SelectionKey.OP_READ);System.out.println("客户端连接成功...");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//处理客户端发来的消息,处理读事件private void dealwithRead(SelectionKey key) {try {SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel)key.channel();System.out.println("读入数据");r_bBuf.clear();//将字节序列从此通道中读入给定的缓冲区r_bBufsc.read(r_bBuf);r_bBuf.flip();String msg = Charset.forName("UTF-8").decode(r_bBuf).toString();if(msg.equalsIgnoreCase("time")) {w_bBuf = ByteBuffer.wrap(getCurrentTime().getBytes("UTF-8"));sc.write(w_bBuf);w_bBuf.clear();} else if(msg.equalsIgnoreCase("bye")) {sc.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("已经与服务器断开连接".getBytes("UTF-8")));sc.socket().close();} else {sc.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes("UTF-8")));}System.out.println(msg);System.out.println("处理完毕...");r_bBuf.clear();try {Thread.currentThread();Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}private String getCurrentTime() {Calendar date = Calendar.getInstance();String time = "服务器当前时间:" + date.get(Calendar.YEAR) + "-" + date.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1 + "-" + date.get(Calendar.DATE) + " " + date.get(Calendar.HOUR) + ":" + date.get(Calendar.MINUTE) + ":" + date.get(Calendar.SECOND);return time;}}?Client:
package org.operamasks.nio;import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStreamReader;import java.net.InetSocketAddress;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;import java.nio.charset.Charset;public class TestClient {public static void main(String[] args) {new MiniClient("localhost", 1982);}}class MiniClient {private SocketChannel sc;private ByteBuffer w_bBuf;private ByteBuffer r_bBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);public MiniClient(String host, int port) {try {InetSocketAddress remote = new InetSocketAddress(host, port);sc = SocketChannel.open();sc.connect(remote);if(sc.finishConnect()) {System.out.println("已经与服务器成功建立连接...");}while(true) {if(!sc.socket().isConnected()) {System.out.println("已经与服务器失去了连接...");return ;}BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));String str = br.readLine();System.out.println("读入一行数据,开始发送...");w_bBuf = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes("UTF-8"));//将缓冲区中数据写入通道sc.write(w_bBuf);System.out.println("数据发送成功...");w_bBuf.clear();System.out.println("接收服务器端响应消息...");try {Thread.currentThread();Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}r_bBuf.clear();//将字节序列从此通道中读入给定的缓冲区r_bBufsc.read(r_bBuf);r_bBuf.flip();String msg = Charset.forName("UTF-8").decode(r_bBuf).toString();System.out.println(msg);}} catch (IOException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}??
参考文章:
1.使用异步I/O大大提高应用程序的性能
2.Linux AIO(异步IO)那些事儿
3.NodeJS代码阅读笔记之libeio
?