Face Normals & Vertex Normals(面法线跟顶点法线的区别)
A face normal is a vector that describesthe direction a polygon is facing(see figure 1)
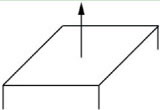

Direct3D or Opengl needs to know the vertex normals so that it can determine the angle at which light strikes a surface,and since lighting calculations are done per vertex, Direct3D or Opengl needsto know the surface orientation(normal) per vertex.
For simple objects such as cubes and spheres, we can see the vertex normals by inspection. For more complex meshes, we need a more mechanical method. Suppose a triangle is formed by the vertices po,p1 and p2, and we need to compute the vertex normal for each of the vertices n0,n1 and n2.
First compute two vectors that lie on the triangle:
p1 - p0 = a
p2 - p0 = b
Then the face normal is :
n = a * b (* means cross product)
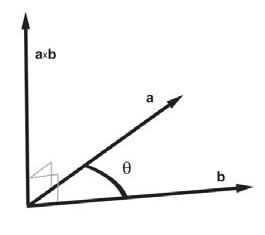
Since each vertex normal is the same as the face normal
n0 = n1 = n2 = n
A better method for finding a vertex normal is normal averaging. To find the vertex normal vn of a vertex v, we find the face normals for all the triangles in the mesh that share vertex v. then vn is given by averaging all of these face normals. Here's an example to illustrate. Suppose three triangles, whose face normals are given by n0,n1 and n2, share the vertex v. Then vn is given by averaging the face normals: vn = (n0 + n1 + n2) /3.
During the transformation stages, it is possible for vertex normals to become non-normal. Therefore, it is best to be safe and renormalize all of your normals after the transformation stages.
Vertex normal can be the same as the face normal (see figure 5)。When we set the vertex normal as the same as the face normal in a .X file, a blue cube will looks like what in below figure, every face has its max brightness when we directly face it.
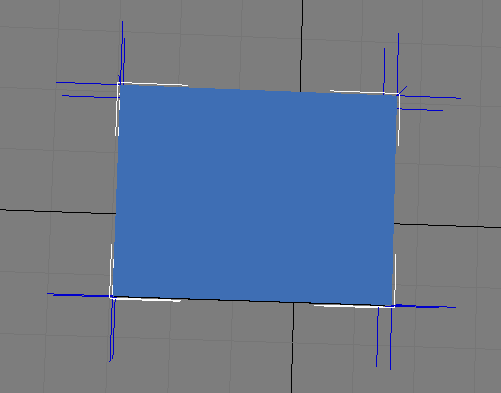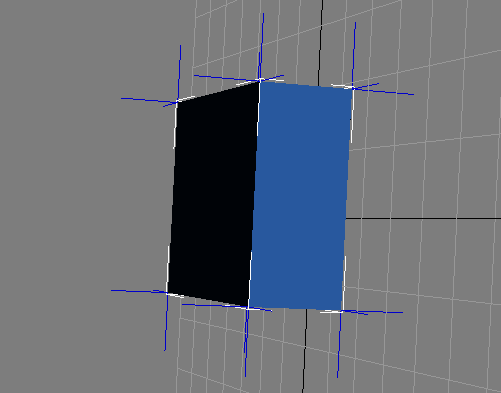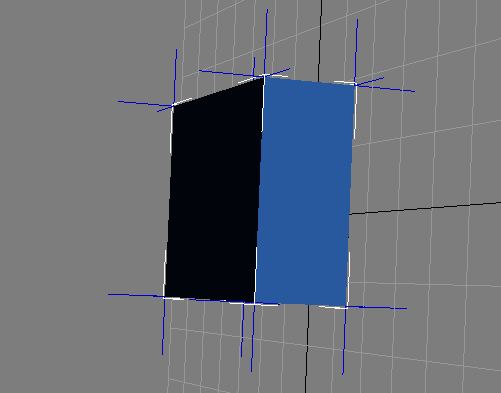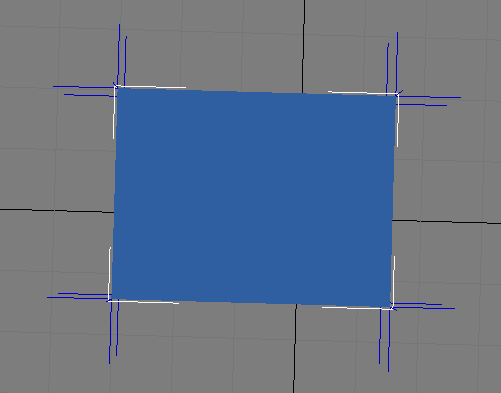
Figure 6: A vertex's vertex normal is average of three face normals
http://www.waitingfy.com/?p=425