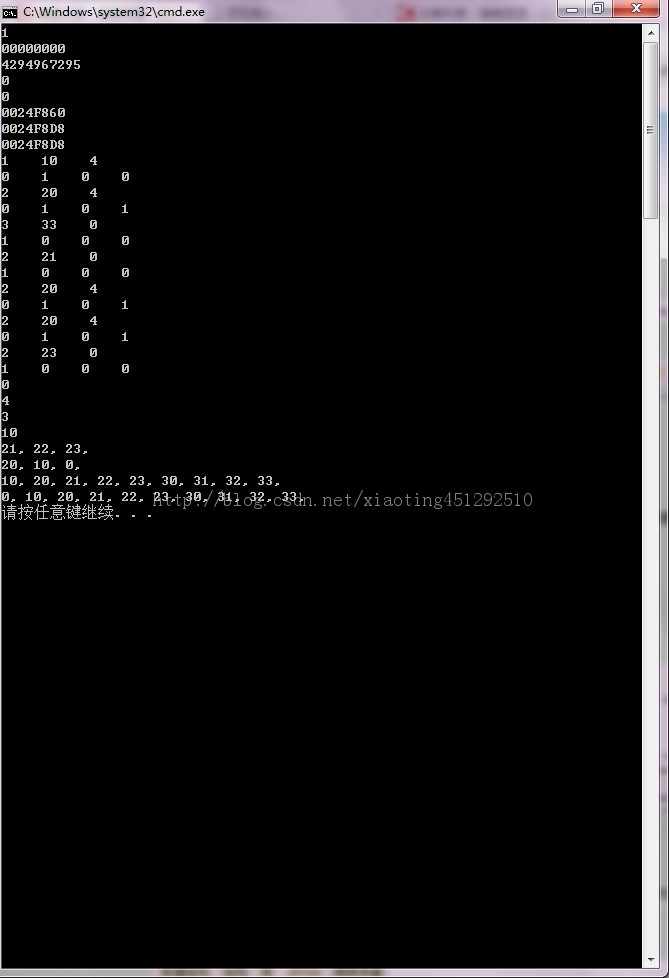
※数据结构※→☆非线性结构(tree)☆============树 链式存储结构(tree list)(十七)
树(tree)
树(tree)是包含n(n>0)个结点的有穷集合,其中:
每个元素称为结点(node);有一个特定的结点被称为根结点或树根(root)。除根结点之外的其余数据元素被分为m(m≥0)个互不相交的集合T1,T2,……Tm-1,其中每一个集合Ti(1<=i<=m)本身也是一棵树,被称作原树的子树(subtree)。树也可以这样定义:树是由根结点和若干颗子树构成的。树是由一个集合以及在该集合上定义的一种关系构成的。集合中的元素称为树的结点,所定义的关系称为父子关系。父子关系在树的结点之间建立了一个层次结构。在这种层次结构中有一个结点具有特殊的地位,这个结点称为该树的根结点,或称为树根。
我们可以形式地给出树的递归定义如下:
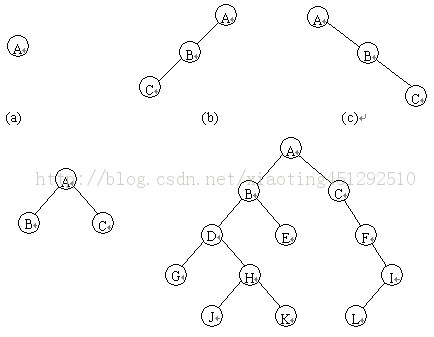
树的四种遍历
1.先序遍历 (仅二叉树)
指先访问根,然后访问孩子的遍历方式
2.中序遍历(仅二叉树)
指先访问左(右)孩子,然后访问根,最后访问右(左)孩子的遍历方式
3.后序遍历(仅二叉树)
指先访问孩子,然后访问根的遍历方式
4.层次遍历
一层一层的访问,所以一般用广度优先遍历。
======================================================================================================
树结点 链式存储结构(tree node list)
结点:
包括一个数据元素及若干个指向其它子树的分支;例如,A,B,C,D等。在数据结构的图形表示中,对于数据集合中的每一个数据元素用中间标有元素值的方框表示,一般称之为数据结点,简称结点。
在C语言中,链表中每一个元素称为“结点”,每个结点都应包括两个部分:一为用户需要用的实际数据;二为下一个结点的地址,即指针域和数据域。
数据结构中的每一个数据结点对应于一个储存单元,这种储存单元称为储存结点,也可简称结点
树结点(树节点):
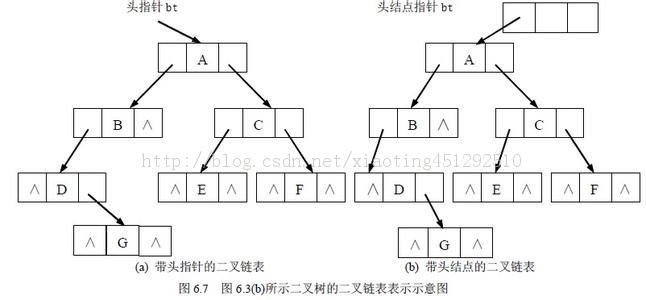
树节点相关术语:
节点的度:一个节点含有的子树的个数称为该节点的度;叶节点或终端节点:度为0的节点称为叶节点;非终端节点或分支节点:度不为0的节点;双亲节点或父节点:若一个结点含有子节点,则这个节点称为其子节点的父节点;孩子节点或子节点:一个节点含有的子树的根节点称为该节点的子节点;兄弟节点:具有相同父节点的节点互称为兄弟节点;节点的层次:从根开始定义起,根为第1层,根的子结点为第2层,以此类推;堂兄弟节点:双亲在同一层的节点互为堂兄弟;节点的祖先:从根到该节点所经分支上的所有节点;子孙:以某节点为根的子树中任一节点都称为该节点的子孙。根据树结点的相关定义,采用“双亲孩子表示法”。其属性如下:
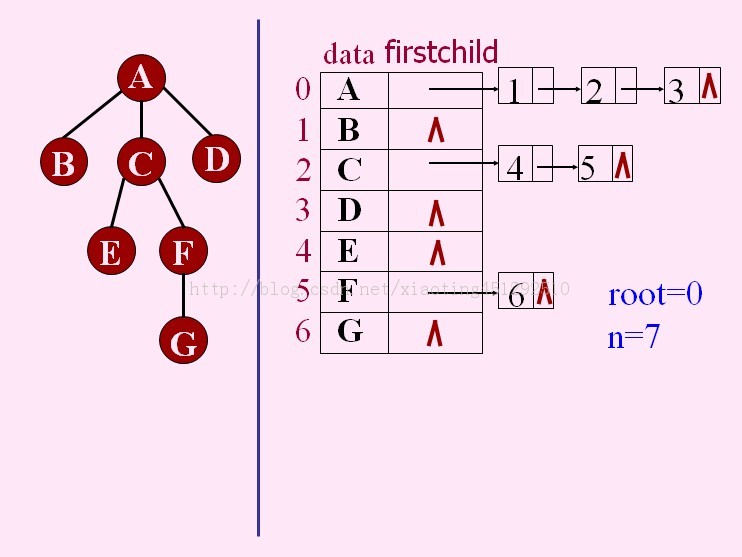
2.孩子表示法
1.多重链表:每个结点有多个指针域,分别指向其子树的根
1)结点同构:结点的指针个数相等,为树的度k,这样n个结点度为k的树必有n(k-1)+1个空链域.
2)结点不同构:结点指针个数不等,为该结点的度d
2.孩子链表:每个结点的孩子结点用单链表存储,再用含n个元素的结构数组指向每个孩子链表
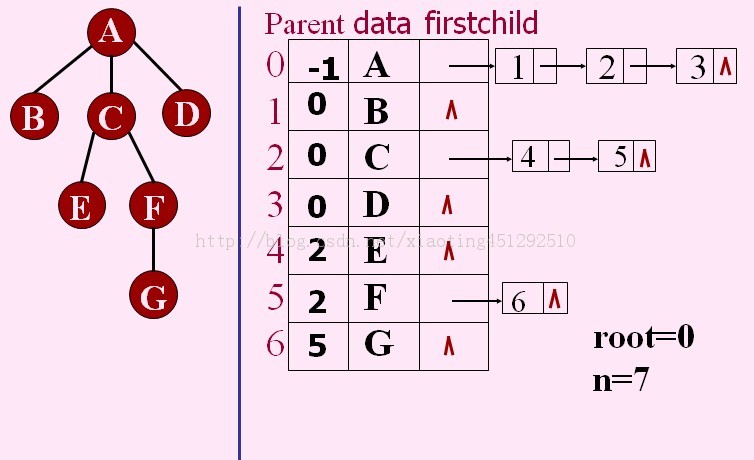
3.双亲孩子表示法
1.双亲表示法,PARENT(T,x)可以在常量时间内完成,但是求结点的孩子时需要遍历整个结构。
2.孩子链表表示法,适于那些涉及孩子的操作,却不适于PARENT(T,x)操作。
3.将双亲表示法和孩子链表表示法合在一起,可以发挥以上两种存储结构的优势,称为带双亲的孩子链表表示法
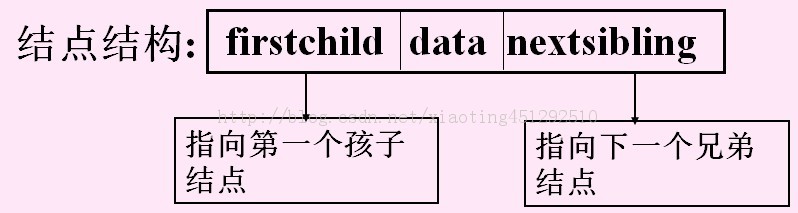
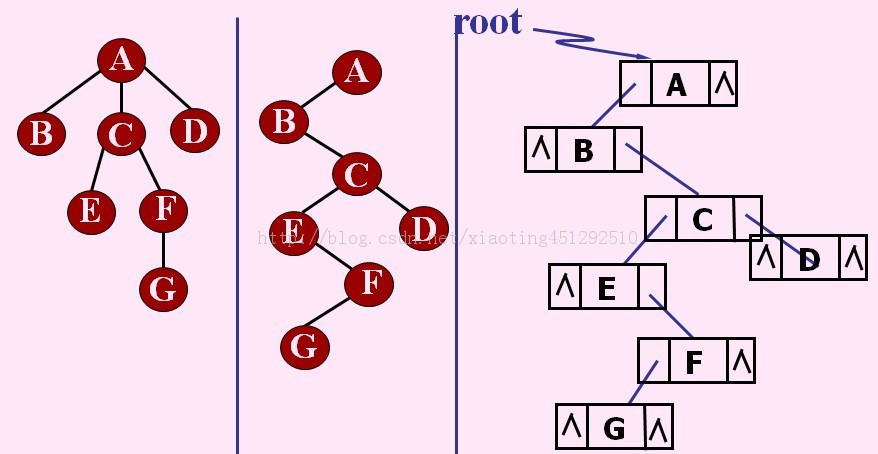
4.双亲孩子兄弟表示法 (二叉树专用)
又称为二叉树表示法,以二叉链表作为树的存储结构。
链式存储结构
在计算机中用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表的数据元素(这组存储单元可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的).
它不要求逻辑上相邻的元素在物理位置上也相邻.因此它没有顺序存储结构所具有的弱点,但也同时失去了顺序表可随机存取的优点.
链式存储结构特点:
1、比顺序存储结构的存储密度小 (每个节点都由数据域和指针域组成,所以相同空间内假设全存满的话顺序比链式存储更多)。
2、逻辑上相邻的节点物理上不必相邻。
3、插入、删除灵活 (不必移动节点,只要改变节点中的指针)。
4、查找结点时链式存储要比顺序存储慢。
5、每个结点是由数据域和指针域组成。~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
以后的笔记潇汀会尽量详细讲解一些相关知识的,希望大家继续关注我的博客。
本节笔记到这里就结束了。
潇汀一有时间就会把自己的学习心得,觉得比较好的知识点写出来和大家一起分享。
编程开发的路很长很长,非常希望能和大家一起交流,共同学习,共同进步。
如果文章中有什么疏漏的地方,也请大家指正。也希望大家可以多留言来和我探讨编程相关的问题。
最后,谢谢你们一直的支持~~~
C++完整个代码示例(代码在VS2005下测试可运行)
AL_TreeNodeList.h
/** @(#)$Id: AL_TreeList.h 51 2013-09-23 10:19:34Z xiaoting $ @briefTree (tree) that contains n (n> 0) nodes of a finite set, where:(1) Each element is called node (node);(2) there is a particular node is called the root node or root (root).(3) In addition to the remaining data elements other than the root node is divided into m (m ≥ 0) disjoint set of T1, T2, ...... Tm-1, wherein each set of Ti (1 <= i <= m ) itself is a tree, the original tree is called a subtree (subtree). Trees can also be defined as: the tree is a root node and several sub-tree consisting of stars. And a tree is a set defined on the set consisting of a relationship. Elements in the collection known as a tree of nodes, the defined relationship is called parent-child relationship. Parent-child relationship between the nodes of the tree establishes a hierarchy. In this there is a hierarchy node has a special status, this node is called the root of the tree, otherwise known as root. We can give form to the tree recursively defined as follows:Single node is a tree, the roots is the node itself.Let T1, T2, .., Tk is a tree, the root node are respectively n1, n2, .., nk. With a new node n as n1, n2, .., nk's father, then get a new tree node n is the new root of the tree. We call n1, n2, .., nk is a group of siblings, they are sub-node n junction. We also said that n1, n2, .., nk is the sub-tree node n.Empty tree is also called the empty tree. Air no node in the tree. The related concepts of tree 1. Degree of tree: a tree, the maximum degree of the node of the tree is called degree; 2. Height or depth of the tree: the maximum level of nodes in the tree; 3. Forests: the m (m> = 0) disjoint trees set of trees called forest; The related concepts of tree node 1.degreedegree node: A node of the subtree containing the number is called the node degree; 2.leafleaf nodes or terminal nodes: degree 0 are called leaf nodes; 3.branchnon-terminal node or branch node: node degree is not 0; 4.parentparent node or the parent node: If a node contains a child node, this node is called its child node's parent; 5.childchild node or child node: A node subtree containing the root node is called the node's children; 6.slibingsibling nodes: nodes with the same parent node is called mutual sibling; 7.ancestorancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch; 8.descendantdescendant nodes: a node in the subtree rooted at any node is called the node's descendants. ////////////////////////////////Sequential storage structure////////////////////////////////////////// Using a set of addresses in the computer storage unit sequentially stores continuous linear form of individual data elements, called the linear order of the table storage structure. Sequential storage structure is a type of a storage structure, the structure is the logically adjacent nodes stored in the physical location of the adjacent memory cells, the logical relationship between nodes from the storage unit to reflect the adjacency. Storage structure thus obtained is stored in order structure, usually by means of sequential storage structure computer programming language (e.g., c / c) of the array to describe. The main advantage of the storage structure in order to save storage space, because the allocation to the data storage unit storing all nodes with data (without regard to c / c language in the array size required for the case), the logical relationship between the nodes does not take additional storage space. In this method, the node can be realized on a random access, that is, each node corresponds to a number, the number can be calculated directly from the node out of the memory address. However, the main disadvantage of sequential storage method is easy to modify the node insert, delete operations, may have to move a series of nodes. Benefits:Random Access table elements. Disadvantages: insert and delete operations need to move elements. @Author $Author: xiaoting $ @Date $Date: 2013-09-23 18:19:34 +0800 (周一, 23 九月 2013) $ @Revision $Revision: 51 $ @URL $URL: https://svn.code.sf.net/p/xiaoting/game/trunk/MyProject/AL_DataStructure/groupinc/AL_TreeList.h $ @Header $Header: https://svn.code.sf.net/p/xiaoting/game/trunk/MyProject/AL_DataStructure/groupinc/AL_TreeList.h 51 2013-09-23 10:19:34Z xiaoting $ */#ifndef CXX_AL_TREELIST_H#define CXX_AL_TREELIST_H#ifndef CXX_AL_LISTSINGLE_H#include "AL_ListSingle.h"#endif#ifndef CXX_AL_QUEUELIST_H#include "AL_QueueList.h"#endif/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////AL_TreeList///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////template<typename T> class AL_TreeList{public:/*** Construction** @paramDWORD dwSize (default value: TREESEQ_DEFAULTSIZE)* @return* @note* @attention*/AL_TreeList();/*** Destruction** @param* @return* @note* @attention */~AL_TreeList();/*** IsEmpty** @param VOID* @return BOOL* @note the tree has data?* @attention*/BOOL IsEmpty() const;/*** GetRootNode** @param* @returnconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>** @note Get the root data* @attention */const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* GetRootNode() const;/*** GetDegree** @param* @returnDWORD* @note Degree of tree: a tree, the maximum degree of the node of the tree is called degree;* @attention */DWORD GetDegree() const;/*** GetHeight** @param* @returnDWORD* @note Height or depth of the tree: the maximum level of nodes in the tree;* @attention */DWORD GetHeight() const;/*** GetNodesNum** @param* @returnDWORD* @note get the notes number of the tree * @attention */DWORD GetNodesNum() const;/*** Clear** @param* @return* @note * @attention */VOID Clear();/*** LevelOrderTraversal** @paramAL_ListSingle<T>& listOrder <OUT>* @returnBOOL* @note Level-order traversal* @attention */BOOL LevelOrderTraversal(AL_ListSingle<T>& listOrder) const;/*** GetSiblingAtNode** @paramAL_ListSingle<T>& listSibling <OUT>* @paramconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @returnBOOL* @note sibling nodes: nodes with the same parent node is called mutual sibling;* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree*/BOOL GetSiblingAtNode(AL_ListSingle<T>& listSibling, const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode) const;/*** GetAncestorAtNode** @paramAL_ListSingle<T>& listAncestor <OUT>* @paramconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @returnBOOL* @note ancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch;* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree*/BOOL GetAncestorAtNode(AL_ListSingle<T>& listAncestor, const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode) const;/*** GetDescendantAtNode** @paramAL_ListSingle<T>& listDescendant <OUT>* @paramconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @returnBOOL* @note ancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch;* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree*/BOOL GetDescendantAtNode(AL_ListSingle<T>& listDescendant, const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode) const;/*** InsertRoot** @paramconst T& tTemplate <IN> * @returnBOOL* @note* @attention*/BOOL InsertRoot(const T& tTemplate);/*** InsertAtNode** @paramAL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @paramDWORD dwIndex <IN>* @paramconst T& tTemplate <IN> * @returnBOOL* @note insert the tTemplate as child tree node to the current tree node (pCurTreeNode) at the position (dwIndex)* @attention if NULL == pCurTreeNode, it will be insert as root tree node, the current tree node must be in the tree*/BOOL InsertAtNode(AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode, DWORD dwIndex, const T& tTemplate);/*** InsertLeftAtNode** @paramAL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @paramconst T& tTemplate <IN> * @returnBOOL* @note insert the tTemplate as child tree node to the current tree node (pCurTreeNode) at the position (left)* @attention if NULL == pCurTreeNode, it will be insert as root tree node, the current tree node must be in the tree*/BOOL InsertLeftAtNode(AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode, const T& tTemplate);/*** InsertRightAtNode** @paramAL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @paramconst T& tTemplate <IN> * @returnBOOL* @note insert the tTemplate as child tree node to the current tree node (pCurTreeNode) at the position (right)* @attention if NULL == pCurTreeNode, it will be insert as root tree node, the current tree node must be in the tree*/BOOL InsertRightAtNode(AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode, const T& tTemplate);/*** GetChildNodeAtNode** @paramconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @paramDWORD dwIndex <IN>* @returnconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>** @note get the current tree node (pCurTreeNode)'s child node at the position (dwIndex)* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree*/const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* GetChildNodeAtNode(const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode, DWORD dwIndex) const;/*** GetChildNodeLeftAtNode** @paramconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @returnconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>** @note get the current tree node (pCurTreeNode)'s child node at the position (left)* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree*/const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* GetChildNodeLeftAtNode(const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode) const;/*** GetChildNodeRightAtNode** @paramconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @returnconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>** @note get the current tree node (pCurTreeNode)'s child node at the position (right)* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree*/const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* GetChildNodeRightAtNode(const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode) const;protected:private:/***Copy Construct** @paramconst AL_TreeList<T>& cAL_TreeList* @return*/AL_TreeList(const AL_TreeList<T>& cAL_TreeList);/***Assignment** @paramconst AL_TreeList<T>& cAL_TreeList* @returnAL_TreeList<T>&*/AL_TreeList<T>& operator = (const AL_TreeList<T>& cAL_TreeList);public:protected:private:DWORDm_dwDegree;DWORDm_dwHeight;DWORDm_NumNodes;AL_TreeNodeList<T>*m_pRootNode;};/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////AL_TreeList////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////*** Construction** @param* @return* @note* @attention*/template<typename T> AL_TreeList<T>::AL_TreeList():m_dwDegree(0xffffffff),m_dwHeight(0x00),m_NumNodes(0x00),m_pRootNode(NULL){}/*** Destruction** @param* @return* @note* @attention */template<typename T> AL_TreeList<T>::~AL_TreeList(){m_dwDegree = 0xffffffff;m_dwHeight = 0x00;m_NumNodes = 0x00;AL_ListSingle<AL_TreeNodeList<T>*> listDescendant;if (NULL != m_pRootNode) {if (TRUE == m_pRootNode->GetDescendant(listDescendant)) {AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pDescendant;for (DWORD dwDelete=0; dwDelete<listDescendant.Length(); dwDelete++) {if (TRUE == listDescendant.Get(pDescendant, dwDelete)) {if (NULL != pDescendant) {delete pDescendant;pDescendant = NULL;}}}}}delete m_pRootNode;m_pRootNode = NULL;}/*** IsEmpty** @param VOID* @return BOOL* @note the tree has data?* @attention*/template<typename T> BOOL AL_TreeList<T>::IsEmpty() const{return (0x00 == m_NumNodes) ? TRUE:FALSE;}/*** GetRootNode** @param* @returnconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>** @note Get the root data* @attention */template<typename T> const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* AL_TreeList<T>::GetRootNode() const{return m_pRootNode;}/*** GetDegree** @param* @returnDWORD* @note Degree of tree: a tree, the maximum degree of the node of the tree is called degree;* @attention */template<typename T> DWORD AL_TreeList<T>::GetDegree() const{return m_dwDegree;}/*** GetHeight** @param* @returnDWORD* @note Height or depth of the tree: the maximum level of nodes in the tree;* @attention */template<typename T> DWORD AL_TreeList<T>::GetHeight() const{return m_dwHeight;}/*** GetNodesNum** @param* @returnDWORD* @note get the notes number of the tree * @attention */template<typename T> DWORD AL_TreeList<T>::GetNodesNum() const{return m_NumNodes;}/*** Clear** @param* @return* @note * @attention */template<typename T> VOID AL_TreeList<T>::Clear(){m_dwDegree = 0xffffffff;m_dwHeight = 0x00;m_NumNodes = 0x00;m_pRootNode = NULL;}/*** LevelOrderTraversal** @paramAL_ListSingle<T>& listOrder <OUT>* @returnBOOL* @note Level-order traversal* @attention */template<typename T> BOOL AL_TreeList<T>::LevelOrderTraversal(AL_ListSingle<T>& listOrder) const{if (TRUE == IsEmpty()) {return FALSE;}if (NULL == m_pRootNode) {return FALSE;}listOrder.Clear();/*AL_ListSingle<AL_TreeNodeList<T>*> listNodeOrder;listNodeOrder.InsertEnd(m_pRootNode);//loop the all nodeDWORD dwNodeOrderLoop = 0x00;AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pNodeOrderLoop = NULL;AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pNodeOrderChild = NULL;while (TRUE == listNodeOrder.Get(pNodeOrderLoop, dwNodeOrderLoop)) {dwNodeOrderLoop++;if (NULL != pNodeOrderLoop) {listOrder.InsertEnd(pNodeOrderLoop->GetData());for (DWORD dwCnt=0; dwCnt<pNodeOrderLoop->GetDegree(); dwCnt++) {pNodeOrderChild = pNodeOrderLoop->GetChild(dwCnt);if (NULL != pNodeOrderChild) {//get the descendantlistNodeOrder.InsertEnd(pNodeOrderChild);}else {//error can not get the descendantreturn FALSE;}}}else {//errorreturn FALSE;}}return TRUE;*/AL_QueueList<AL_TreeNodeList<T>*> queueOrder;queueOrder.Push(m_pRootNode);AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pNodeOrderLoop = NULL;AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pNodeOrderChild = NULL;while (FALSE == queueOrder.IsEmpty()) {if (TRUE == queueOrder.Pop(pNodeOrderLoop)) {if (NULL != pNodeOrderLoop) {listOrder.InsertEnd(pNodeOrderLoop->GetData()); for (DWORD dwCnt=0; dwCnt<pNodeOrderLoop->GetDegree(); dwCnt++) {pNodeOrderChild = pNodeOrderLoop->GetChild(dwCnt);if (NULL != pNodeOrderChild) {queueOrder.Push(pNodeOrderChild);}}}else {return FALSE;}}else {return FALSE;}}return TRUE;}/*** GetSiblingAtNode** @paramAL_ListSingle<T>& listSibling <OUT>* @paramconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @returnBOOL* @note sibling nodes: nodes with the same parent node is called mutual sibling;* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree*/template<typename T> BOOL AL_TreeList<T>::GetSiblingAtNode(AL_ListSingle<T>& listSibling, const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode) const{if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {return FALSE;}AL_ListSingle<AL_TreeNodeList<T>*> listTreeNodeSibling;if (FALSE == pCurTreeNode->GetSibling(listTreeNodeSibling)) {return FALSE;}//clear listSibling listSibling.Clear();AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pTreeNodeSibling = NULL;for (DWORD dwCnt=0; dwCnt<listTreeNodeSibling.Length(); dwCnt++) {if (TRUE == listTreeNodeSibling.Get(pTreeNodeSibling, dwCnt)) {if (NULL != pTreeNodeSibling) {//inset the data to listSiblinglistSibling.InsertEnd(pTreeNodeSibling->GetData());}else {//errorreturn FALSE;}}else {//errorreturn FALSE;}}return TRUE;}/*** GetAncestorAtNode** @paramAL_ListSingle<T>& listAncestor <OUT>* @paramconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @returnBOOL* @note ancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch;* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree*/template<typename T> BOOL AL_TreeList<T>::GetAncestorAtNode(AL_ListSingle<T>& listAncestor, const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode) const{if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {return FALSE;}AL_ListSingle<AL_TreeNodeList<T>*> listTreeNodeAncestor;if (FALSE == pCurTreeNode->GetAncestor(listTreeNodeAncestor)) {return FALSE;}//clear listAncestor listAncestor.Clear();AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pTreeNodeAncestor = NULL;for (DWORD dwCnt=0; dwCnt<listTreeNodeAncestor.Length(); dwCnt++) {if (TRUE == listTreeNodeAncestor.Get(pTreeNodeAncestor, dwCnt)) {if (NULL != pTreeNodeAncestor) {//inset the data to listSiblinglistAncestor.InsertEnd(pTreeNodeAncestor->GetData());}else {//errorreturn FALSE;}}else {//errorreturn FALSE;}}return TRUE;}/*** GetDescendantAtNode** @paramAL_ListSingle<T>& listDescendant <OUT>* @paramconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @returnBOOL* @note ancestor node: from the root to the node through all the nodes on the branch;* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree*/template<typename T> BOOL AL_TreeList<T>::GetDescendantAtNode(AL_ListSingle<T>& listDescendant, const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode) const{if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {return FALSE;}AL_ListSingle<AL_TreeNodeList<T>*> listTreeNodeDescendant;if (FALSE == pCurTreeNode->GetDescendant(listTreeNodeDescendant)) {return FALSE;}//clear listAncestor listDescendant.Clear();AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pTreeNodeDescendant = NULL;for (DWORD dwCnt=0; dwCnt<listTreeNodeDescendant.Length(); dwCnt++) {if (TRUE == listTreeNodeDescendant.Get(pTreeNodeDescendant, dwCnt)) {if (NULL != pTreeNodeDescendant) {//inset the data to listSiblinglistDescendant.InsertEnd(pTreeNodeDescendant->GetData());}else {//errorreturn FALSE;}}else {//errorreturn FALSE;}}return TRUE;}/*** InsertRoot** @paramconst T& tTemplate <IN> * @returnBOOL* @note* @attention*/template<typename T> BOOL AL_TreeList<T>::InsertRoot(const T& tTemplate){return InsertAtNode(NULL, 0x00, tTemplate);}/*** InsertAtNode** @paramAL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @paramDWORD dwIndex <IN>* @paramconst T& tTemplate <IN> * @returnBOOL* @note insert the tTemplate as child tree node to the current tree node (pCurTreeNode) at the position (dwIndex)* @attention if NULL == pCurTreeNode, it will be insert as root tree node, the current tree node must be in the tree*/template<typename T> BOOL AL_TreeList<T>::InsertAtNode(AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode, DWORD dwIndex, const T& tTemplate){AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pTreeNode = NULL;if (TRUE == IsEmpty()) {if (NULL != pCurTreeNode) {//error can not insert to the current node pCurTreeNode, is not exist in the treereturn FALSE;}else {pTreeNode = new AL_TreeNodeList<T>;if (NULL == pTreeNode) {return FALSE;}pTreeNode->SetData(tTemplate);pTreeNode->SetLevel(0x00);m_pRootNode = pTreeNode;m_dwDegree = 0x00;m_dwHeight = 0x00;//empty tree 0xffffffff (-1)m_NumNodes++;return TRUE;}}if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {return FALSE;}//inset to the current tree nodepTreeNode = new AL_TreeNodeList<T>;if (NULL == pTreeNode) {return FALSE;}pTreeNode->SetData(tTemplate);pTreeNode->SetLevel(pCurTreeNode->GetLevel() + 1);if (FALSE == pCurTreeNode->Insert(dwIndex, pTreeNode)) {delete pTreeNode;pTreeNode = NULL;return FALSE;}DWORD dwCurNodeDegree = 0x00;//loop all node to get the current node degreeif (pCurTreeNode->GetDegree() > m_dwDegree) {m_dwDegree = pCurTreeNode->GetDegree();}if (pTreeNode->GetLevel() > m_dwHeight) {m_dwHeight =pTreeNode->GetLevel();}m_NumNodes++;return TRUE;}/*** InsertLeftAtNode** @paramAL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @paramconst T& tTemplate <IN> * @returnBOOL* @note insert the tTemplate as child tree node to the current tree node (pCurTreeNode) at the position (left)* @attention if NULL == pCurTreeNode, it will be insert as root tree node, the current tree node must be in the tree*/template<typename T> BOOL AL_TreeList<T>::InsertLeftAtNode(AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode, const T& tTemplate){return InsertAtNode(pCurTreeNode, 0x00, tTemplate);}/*** InsertRightAtNode** @paramAL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @paramconst T& tTemplate <IN> * @returnBOOL* @note insert the tTemplate as child tree node to the current tree node (pCurTreeNode) at the position (right)* @attention if NULL == pCurTreeNode, it will be insert as root tree node, the current tree node must be in the tree*/template<typename T> BOOL AL_TreeList<T>::InsertRightAtNode(AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode, const T& tTemplate){return InsertAtNode(pCurTreeNode, pCurTreeNode->GetDegree(), tTemplate);}/*** GetChildNodeAtNode** @paramconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @paramDWORD dwIndex <IN>* @returnconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>** @note get the current tree node (pCurTreeNode)'s child node at the position (dwIndex)* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree*/template<typename T> const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* AL_TreeList<T>::GetChildNodeAtNode(const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode, DWORD dwIndex) const{if (NULL == pCurTreeNode) {return NULL;}return pCurTreeNode->GetChild(dwIndex);}/*** GetChildNodeLeftAtNode** @paramconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @returnconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>** @note get the current tree node (pCurTreeNode)'s child node at the position (left)* @attention the current tree node must be in the tree*/template<typename T> const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* AL_TreeList<T>::GetChildNodeLeftAtNode(const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode) const{return GetChildNodeAtNode(pCurTreeNode, 0x00);}/*** GetChildNodeRightAtNode** @paramconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode <IN>* @returnconst AL_TreeNodeList<T>** @note get the current tree node (pCurTreeNode)'s child node at the position (right)* @attention*/template<typename T> const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* AL_TreeList<T>::GetChildNodeRightAtNode(const AL_TreeNodeList<T>* pCurTreeNode) const{return GetChildNodeAtNode(pCurTreeNode, pCurTreeNode->GetDegree());}#endif // CXX_AL_TREELIST_H/* EOF */