排序算法——堆和堆排序
一、什么是堆
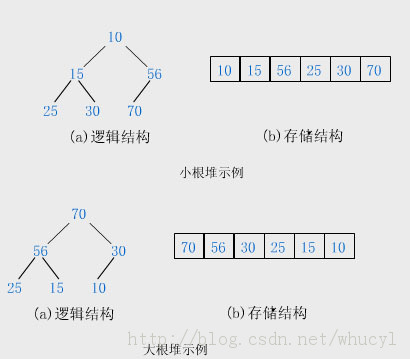
- 堆实际上是一棵完全二叉树;对于n个关键字序列 [ K0,K1,…,K(n-1) ],一般采用数组方式存储;
任何一非叶节点的关键字满足如下性质:若ki<=k(2i+1)且ki<=k(2i+2)(0≤i≤ n-1),称之为小根堆;若ki>=k(2i+1)且ki>=k(2i+2)(0≤i≤ n-1),称之为大根堆.
堆排序思想 充分利用了堆顶关键字最大或最小的特性,从而可以快速选取一组数中的最大值或最小值。
堆排序分为两个步骤:构建堆 和 调整堆。
以大根堆为例,堆排序过程如下:
三、算法实现将初始待排序关键字序列(R0,R1....Rn-1)构建成大顶堆,此堆为初始的无序区;将堆顶元素与堆尾元素交换,堆的长度减1, 此时得到新的无序区和新的有序区;由于交换后新的堆顶可能违反堆的性质, 因此需要对当前无序区调整为新堆;不断重复过程2和3直到有序区的元素个数为n-1,则整个排序过程完成
堆的基本操作分为向上调整和向下调整,利用向上调整操作构建堆,堆顶元素和堆尾交换后,堆长度减1,利用向下调整操作从堆顶开始调整生成新堆。#include <iostream>using namespace std;inline void swap(int arr[], int a, int b) {int temp = arr[a];arr[a] = arr[b];arr[b] = temp;}// 向上调整堆:从堆尾开始向堆顶调整// arr: 堆数组指针//n: 堆尾元素位置void shiftUp(int arr[], int n) {if (n < 1) {return;}int b = (n - 1) / 2;int a = n;while (a > 0) {if (arr[a] > arr[b]) {swap(arr, a, b);a = b;b = (b - 1) / 2;} else {break;}}}// 向下调整堆:从堆顶开始向堆尾调整// arr: 堆数组指针//n: 堆尾元素位置void shiftDown(int arr[], int n) {if (n < 1) {return;}int a, b = 0;int maxLeaf = (n - 1) / 2;while (b <= maxLeaf) {a = 2 * b + 1;if (a < n && arr[a] < arr[a + 1]) {a++;}if (arr[b] < arr[a]) {swap(arr, b, a);b = a;} else {break;}}}// 堆排序算法//arr: 待排序的数组指针//len: 数组长度void heapSort(int* arr, int len) {int index;// 构建堆for (index = 1; index < len; index++) {shiftUp(arr, index);}// 调整堆for (index = len - 1; index > 0;) {swap(arr, 0, index);index--;shiftDown(arr, index);}}// 测试算法int main() {int arr[] = { 213, 43, 43, 123, 45, 52, 67, 234, 452, 5, 67 };int len = 11;cout << "Before sorting:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {cout << arr[i] << "\t";}cout << endl << endl;heapSort(arr, len);cout << "After Sorting:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {cout << arr[i] << "\t";}cout << endl;return 0;}执行结果如下:
四、算法分析
堆排序时间复杂度为: O(n*log2(n))堆排序空间复杂度为: O(1)
